Security Alert: HrServ Web Shell is Hacked by APT, Breach of Windows Systems

Cybersecurity specialists at Securelist found that the DLL file known as hrserv.dll, a previously unidentified web shell, displays advanced capabilities, including unique encoding techniques for client connection and in-memory execution.
Following the data analysis, comparable variations created in 2021 were found, suggesting a possible connection between these disparate instances of detrimental activity.
A malicious software or program known as a HrServ web shell permits remote server administration, granting unauthorized access and control.
Hackers target web shells to obtain unauthorized access to a server or website. This allows them to run commands, upload and download data, and modify the system for malevolent objectives such as Theft of data and initiating new malicious activities.
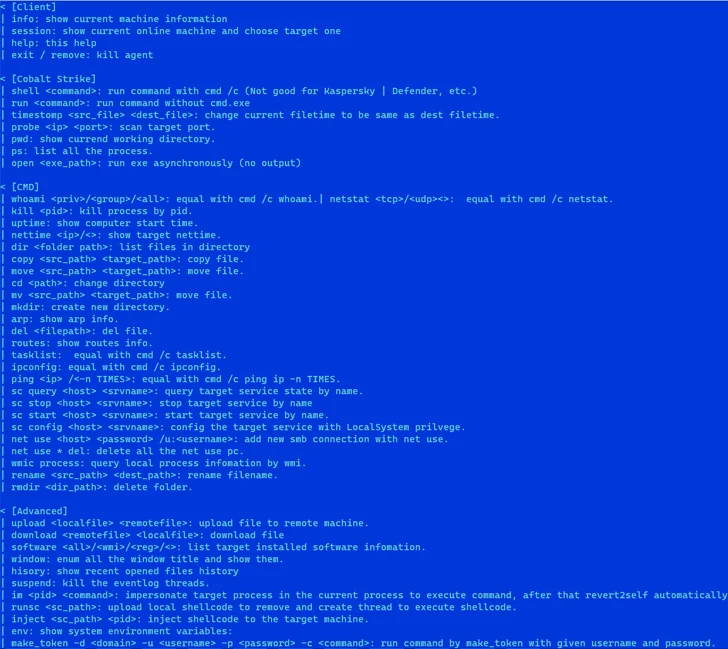
HrServ Web Shell
By generating a “MicrosoftsUpdate” scheduled task, PAExec.exe initiates a.BAT file. The script creates a registry service using’ copies $public\hrserv.dll to System32 and then launches the recently formed service. HrServ first registers a handler for service before utilizing custom encoding to start an HTTP server -Base64, FNV1A64.
The DLL uses the NID cookie in addition to activating certain functionalities in response to the ‘cp’ GET parameter in HTTP requests. The naming conventions are like Google’s and might mask malicious activities in network data, making identification difficult.
Code execution is triggered by a cp value of 6, and in a specific case when the cp value is unknown, a versatile implant initiates in system memory.
Along with Creating a File in “% temp%,” it carries out the Subsequent Steps:
- Obtains Registry Information.
- Acts in Response to it.
- Keeps Track of Output in the File.
The researchers found that the sample under analysis is a capable web shell. Based on the compilation timestamps, its origins are at least 2021. This is a more advanced version of malware that can start in-memory operations. When observed, temporary files and registry modifications are used to establish communication.
Notably, the memory implant and web shell use various strings under different scenarios. The memory implant also has a well-designed help message. Furthermore, the memory implant has a well-designed help message. When these elements are considered, the malware’s traits align with financially motivated fraudulent activity.
That said, there are certain parallels between its operating approach and the behavior of APT. Aside from this, security experts could not relate the TTPs to any identifiable threat actors.
