Brute Force Attack: Types, Examples, Tools, Prevention

If you use the Internet or have an online presence, you are probably vulnerable to security breaches or attacks. One such attack that is very common is the Brute Force attack.
In fact, of all the breaches caused by hacking, 80% of breaches involve brute force or the use of lost or stolen credentials.
This is a popular technique by which cybercriminals get unauthorized access to an account or resource. But how?
All the questions will be answered in this blog.
What is a Brute Force Attack?
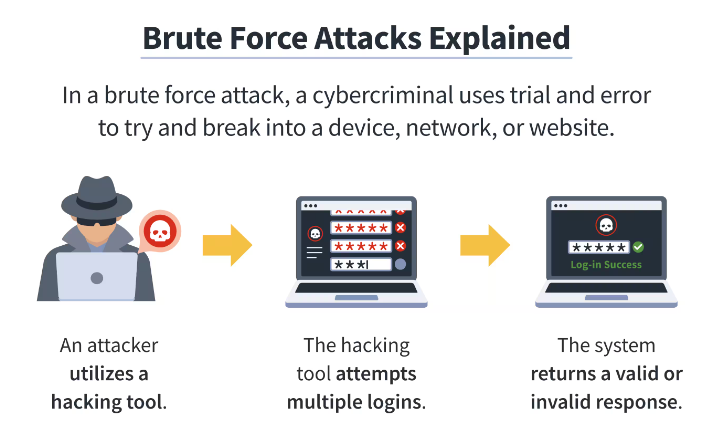
The brute force attack (also known as brute-force cracking) is a cyber-attack in which the hacker hacks the user account by guessing ID and password through different combinations.
In simple terms, it is a trial-and-error method used to decode sensitive data. However, this is an old cyberattack method, but still, in 2024, it is a popular tactic that hackers use.
What differentiates brute force from other cyber attacks is that it does not demand any intellectual strategy, but the hacker tries multiple usernames and passwords until they find the right login information.
This can be perceived as when a thief tries to break a safe by attempting every possible combination until it opens.
Types of Brute Force Attacks
Brute Force Attacks are of different types that allow hackers to steal user data.
Simple or Traditional Brute Force Attacks
This attack happens when hackers’ guesswork makes them log in to a user’s account successfully. Simple brute force attacks are done through standard password combinations or personal identification number (PIN) codes.
The individuals who majorly become targets are the ones who use very easy passwords, like “password123,” “1234,” or use the same password for multiple websites.
Dictionary Attacks
Instead of generating random combinations, the attacker guesses the password using a predefined list of commonly used passwords or dictionary words. They analyze users’ social media profiles to find their interests and see if certain words pop out in more focused dictionary attacks.
However, the chances of this attack happening are very low because it is time-consuming and requires extra effort.
Hybrid Brute Force Attacks
A hybrid brute force attack combines the above two attacks, Traditional and Dictionary attacks. This procedure entails augmenting dictionary words with special characters or numbers to find the account login information.
For instance, they might try variations like “P@ssw0rd2023” or “Sunshine! 123.”
Reverse Brute Force Attacks
Reverse brute attacks happen when hackers already own your old password, which they found through a network breach. This can be further used to search for a matching login credential through calculated guesses.
Credential Stuffing
In this attack, hackers take advantage of individuals’ habit of using the exact same username and password (p/w) across different accounts.
Attackers get their hands on a bunch of username and password combos from one source, which they use to gain access to additional user accounts.
Given that individuals repeat passwords across numerous domains, it’s no surprise that why these attacks are so successful.
How Do Brute Force Attacks Occur?
Brute force attacks occur when hackers try to crack passwords by guessing every possible combination until they find the correct one. Here’s how!
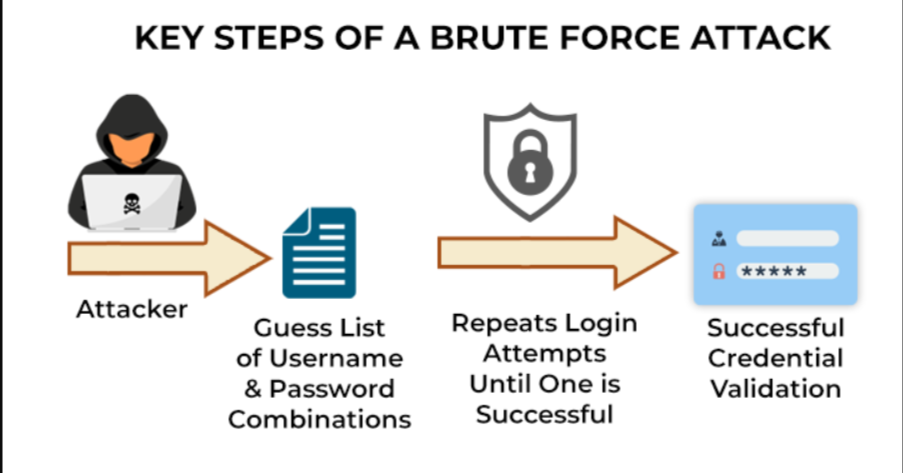
- Firstly, attackers target a system or account they want to break into.
- Then, they gather information about the target, such as usernames, email addresses, or any other relevant details that could help them guess the password.
- Now, according to the target and available resources, hackers choose the best brute force attack method, like a simple dictionary, a hybrid, or even a reverse brute force attack.
- Using specialized software or scripts, attackers begin the brute force attack. How? They first start with different combinations of common passwords or dictionary words.
- As the attack progresses, the attacker continuously tests the guessed credentials to see if they grant access to the target system or account. Sometimes, it’s quick, but other times, it can take a long time, especially if the password is really complex.
- Once the password is cracked, they can access the account or system and steal the individual’s personal information.
Brute force attack comes with a lot of consequences, such as:
- If a system gets compromised, attackers gain access to user accounts which they further use for manipulation, data theft, and other malicious activities.
- Loss of individual’s sensitive financial information
- Loss of intellectual property, like trade secrets, proprietary information, or research data.
- If an organization fails to protect user data, they have to face legal and regulatory consequences under different acts, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
- Damage to the organization’s reputation and disruption in tasks.
What is the Difference between a Password Attack and a Brute Force Attack?
There is a very thin line difference between a password attack and a brute force attack, as both are used by hackers to maliciously hack a user account.
Here’s how they differentiate.
Password Attack is a broad term that encompasses various methods, like Phishing, Man-in-the-Middle Attacks, Keylogging, Credential Stuffing, etc, to obtain passwords or access to protected systems.
On the other hand, Brute Force Attack is a specific type of password attack where hackers try every possible combination of characters or words until the correct password is discovered.
To sum up, all brute force attacks are password attacks; not all password attacks involve brute force methods.
Popular Tools For Performing Brute Force Attack
Guessing a user’s account password is not as easy as it seems, especially if the passwords are strong. That’s why cybercriminals use different brute-force attack tools to make guessing credentials and finding combinations easier. These are further used to:
- Identifying Weak Passwords,
- Running Character Combinations
- Deploying Dictionary Attacks and
- Decrypting Password Data
Some of the commonly used brute force attack tools include:
John the Ripper:
It is one of the oldest and most widely used password-cracking tools, and it is known for its versatility and ability to crack passwords using various decryption techniques. John the Ripper runs seamlessly on 15 different platforms, including Unix, Windows, and OpenVMS.
Aircrack-ng:
It is a set of tools that can be used on Windows, iOS, Linux, and Android to breach wireless networks’ fake access points and packet injection.
Hashcat:
Another powerful password-cracking tool, Hashcat, is known for its speed and support for multiple hashing algorithms. It can perform brute force attacks, dictionary attacks, and rule-based attacks to crack passwords stored in hashed formats.
Real-life Examples of Brute Force Attacks
Here are some of the real-life cases when brute-force attacks lead to huge security breaches.
Dunkin’ Donuts (2015)
The famous coffee franchise Dunkin’ Donuts suffered a brute-force attack in 2015. The hackers tried various password combinations and successfully accessed about 19,715 user accounts within just five days. They stole significant sums of money from the compromised accounts.
But this is not it! The situation became more complicated because Dunkin’ Donuts failed to promptly inform its customers about the breach.
This lack of transparency led to a lawsuit against the company and resulted in $650,000 in fines and damages. Also, the company was forced to reset all user passwords and upgrade security protocols.
Alibaba (2016)
It is very shocking to see Alibaba’s name on this list, but yes, it’s true that the popular e-commerce platform became a victim of the brute force attack in 2016. This put the accounts of approximately 21 million users at risk.
This attack occurred over a two-month period, from October to November, and resulted in unauthorized access to the usernames and passwords of 99 million users.
“123456” is the most commonly used password that people use and, unfortunately, become cyberattack victims. The same happened here!
The investigations revealed that the attack was caused by two main factors: password reuse and weak password practices.
This breach highlights the critical importance of strong password management practices for both users and companies.
Magento (2018)
Another popular e-commerce platform, Magento faced a brute force attack in 2018 that compromised its admin panels.
Researchers who looked into the attack found something alarming: they discovered over 1,000 account credentials related to Magento on the dark web. The hackers’ goal was to steal credit card numbers from users and infect their devices with malware to mine cryptocurrencies.
To prevent this from happening again, Magento advised its users to make stronger passwords.
GitHub (2013)
In 2013, GitHub, a popular platform for hosting software code, became the victim of a brute force attack. This attack targeted several GitHub users, potentially compromising their accounts and sensitive data.
The attack was made possible because many users had weak passwords, which made it easier for hackers to break into their accounts. As a result, sensitive information ended up being leaked.
One notable aspect of this attack was that the hackers used nearly 40,000 individual IP addresses to avoid detection by GitHub’s security measures.
The best part is that the company took prompt action, informed users about the breach, and asked them to update their passwords with stronger combinations.
Northern Irish Parliament (2018)
A brute force attack compromised the Northern Irish Parliament’s member’s accounts in 2018. The hackers accessed the mailboxes of assembly members by trying several passwords, which resulted in deleted accounts and gaining access to confidential data.
How to Prevent Brute Force Attack?
Below are some of the strategies explained that can be used to combat brute force attacks.
Use Strong Passwords
Using strong passwords is important for both individuals and companies as it can significantly lower the chances of a successful brute-force attack.
Here are some of the practices that must be followed while making a password.
Don’t use the same password for multiple accounts
This is a very common practice that everyone follows because they find it easier to log in to multiple accounts by using the same password.
But let us tell you, doing so can make you a target of brute force attacks. Because if the hacker gets access to your one account, they can easily access the other as well! Never use the same password for multiple accounts.
Never use Passwords that are Easy to Guess
Some studies revealed that the most commonly used passwords are “123456,” “123456789,” and “qwerty.” These are definitely very easy to memorize, but the bitter truth is that hackers can easily guess them.
So always make a password of at least 12 to 15 characters, including a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols. For instance, “DHcjBxR2MRk1uVO.”
Further, you can also make personalized passwords from your favorite song or food. Always omit some words and use only the initial letter. For instance, you can replace “seed” with “sd” to create a unique string.
Use a Password Manager
Creating strong passwords can be hectic, but not when you use a password manager. It helps you create long and complex passwords for every account.
The best part? These will be stored automatically on your phone, tablet, or computer, so there is no need to memorize them.
Enforce Secure & Encrypted Connections Among Employees
This practice is especially important for business owners who run a company. SSL/TLS certificates are always used to ensure security over the internet, but enforcing secure and encrypted connections among employees is often overlooked.
So, it’s vital to use virtual private networks (VPNs), especially for remote work scenarios. VPNs create encrypted tunnels between the user’s device and the corporate network, regardless of their physical location. This not only protects data in transit but also ensures that remote connections are kept separate from potentially insecure networks.
By using VPN connectivity and proper VPN configuration, organizations can mitigate the risk of brute-force attacks.
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is an additional security tactic that requires users to authenticate using two types of identification before accessing their accounts.
This involves something the user knows (such as a password) and something they have (like a mobile phone or security token).
Also Read: What Is a Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)? Difference Between 2FA & MFA
MFA reduces the risk of unaccredited access to accounts. How?
Even if the hacker manages to guess or steal a user’s password, they still need a second form of identification to gain access, which is not that easy!
However, hackers will always be hackers! Despite MFA’s effectiveness, they have developed methods to bypass it. So, it is the user’s responsibility to remain vigilant and protect their accounts effectively.
Limit Login Attempts
It is one of the best ways by which brute force attacks can be failed, i.e., limiting login attempts.
It caps the number of times someone can try to log in to an account with the wrong password. After a certain number of failed attempts, the system locks them out for a while. Each time they fail again, the lockout period gets longer.
This makes it much harder for attackers to guess your password through trial and error. Even if they try thousands of combinations, they won’t be able to log in after a few failed attempts.
Monitoring & Logging
Monitoring and logging are crucial practices for effectively detecting and responding to security threats. Actively monitoring system activity helps identify unusual behavior, such as repeated failed or unauthorized login attempts.
Logging records important information about these events, including the user’s ID, IP address, date, time, and details of the attempted login. This data can be used for analyzing patterns and identifying potential security risks.
Use CAPTCHA
Automated software applications can not break CAPTCHAs; only a human mind is capable of doing so. Now, most brute-force attacks rely on automated software that cannot pass CAPTCHA challenges.
By adding a CAPTCHA to the login procedure, websites can make it tough for attackers to sneak in.
Update Software and Firmware
Outdated software and firmware are some of the main reasons why brute force attacks are successful. When software or firmware is outdated, it can have vulnerabilities that hackers exploit to break into the system. So, regularly update these components to keep the system safe from cybercriminals. It’s like staying one step ahead of them!
The Bottom Line
To conclude, brute force attacks have a 100 percent success rate. Real-life examples such as the Alibaba and Dunkin’ Donuts breaches highlight the real-world impact of these attacks. So, it’s better to follow the proper security measures than to be a victim.
Get Web Security Services from Certera to enhance the safety of your website, software, apps, and APIS. From website vulnerability scanning to API penetration testing, we offer a complete suite of security services.
