What Is a Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)? Difference Between 2FA & MFA
Cyber threats are continuously evolving as everyone is moving towards an era of digital interventions. Now, various defense mechanisms are coming into play to combat these threats, and among them, one such is multi-factor authentication, which has gained significant traction in recent years.
60% of large and global enterprises and 80% of small and mid-sized organizations are adopting MFA capabilities to secure their organization’s accounts.
~ According to a Survey by Gartner
So, if you want to join these numbers, this blog is for you! It will explain how MFA works, its authentication methods, and how that can be further used for your company’s enhanced security.
Let’s get started!
What is Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-factor authentication (or MFA) is a multi-layered security system that helps verify a user, application, or device through several identifiers.
Let’s understand this term in a better way with some examples.
- Have you ever come across the codes created by mobile apps?
- When accessing a specific website, you are first asked to answer some personal security questions.
- Sometimes, codes have been sent to an email address to perform a particular action.
All the instances above are implemented in day-to-day scenarios to decrease the chances of a cyber attack. Simply put, MFA requires one or more verification factors for enhanced security instead of just a username and password.
Now, let’s understand how it works to provide that security!
How Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Works?
When an individual logs in to an account, their username and password are generally required for this purpose. Right?
Now the question arises: What is the role of Multi-Factor Authentication? How it works?
Don’t worry! We are here to answer everything!
In general, here’s the process.
- To access an account, the user enters a username and password.
- Then, MFA works by requesting multiple forms of ID from the user, which includes a one-time password (OTP), SMS, or biometric information such as a fingerprint/face scan. Once the system verifies the password, it automatically connects to the other steps.
Importance/Benefits of MFA
Provides Enhanced Level of Security
- A report by Microsoft entails that MFA can prevent 99.9% of hacker attacks, which is one of its major benefits, “Enhanced level of security.” It requires users to provide multiple credentials before accessing accounts. This will be helpful when the hackers try to hack your account, as they can only access the data with different credentials.
- Talking about large companies that store consumers’ confidential information should create a layered defense, whether mobile, biometric, or physical. This will help track individuals coming in and out of their system, which could be in hundreds or thousands.
Compatible with Single Sign-On (SSO) Solutions
- An industry-compliant MFA is compatible with an SSO solution and embedded into applications. This compatibility ensures no need to create multiple complex passwords for different applications.
- Simply put, MFA with SSO reduces friction to verify the user identity and reduces the risk of losing data due to password misplacement.
Adherence To Regulatory Compliances
- MFA implementation is required to comply with certain industry regulations. For instance, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) and Payments Service Directive 2 (PSD2) need multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
- Similarly, MFA helps to maintain compliance with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) & CJIS.
Compliant With Different Use Cases
- Situations like high-value transactions and accessing sensitive data from unknown networks require high-level security. Here’s the role of Adaptive MFA comes into play.
- This approach evaluates potential risks using contextual and behavioral information, such as geolocation, IP addresses, and the duration since the last authentication.
Combat Password Fatigue
- According to a report by NordPass, individuals are tasked with remembering anywhere between 70 to 80 passwords. You must be relating to these stats, right? With so many passwords to remember, keeping track is a struggle.
- Now, what ends up happening is consumers either use the same password for different accounts or come up with easy-to-guess ones. Unfortunately, both practices increase the risk of password-related security breaches.
- Muti-factor authentication can be used as a robust solution to address this challenge. Here’s how! 1) Add an additional layer of security. 2) Minimize the impact of password fatigue. 3) Strengthens the defense against potential breaches.
- Even if the user uses straightforward or repetitive passwords, MFA introduces an extra authentication step that makes it difficult for hackers to undertake vulnerabilities.
- Overall, MFA adoption can reduce the frequency of password reset requests. As a result, it enhances security & streamlines operational efficiency, which saves both time and resources for businesses.
Common Types of Multi-Factor Authentication
The three common types of MFA used for authentication include:
Something You Know (Knowledge)
- “Something You Know” is the most basic form of authentication, also known as “Knowledge-based authentication.”
- It typically involves a secret that only the user knows, which commonly includes passwords, pins, or answers to security questions.
- KBA is generally of two types, i.e., Static & Dynamic. Among these two, the dynamic one is more secure as its security questions are generated in real-time and based on regularly updated data records (e.g., credit transactions).
Something You Have (Possession)
- This form of authentication involves something physical that the user possesses, including smartphones, hard tokens, soft tokens, key fobs, and smart cards. One such is Google Authenticator, a good example of an app on the phone as a token.
- The “Something You Have” authentication type includes a pop-up notification confirmation on a mobile phone, insertion of a security card, or the deprecated OTP, which could be received via text message or email.
Something You Are (Inheritance)
- “Something You Are” authentication is based on the users’ behavior or biological traits, including fingerprints, palm scanning, facial recognition, retina scans, iris scans, and voice verification.
- This is the most secure authentication method that even a hacker can’t easily steal the data and more quicker than waiting for an OTP to be generated.
- This method requires an up-to-date smart device to download a biometric authenticator app. As a result, it will become a disadvantage for users using outdated versions of smartphones.
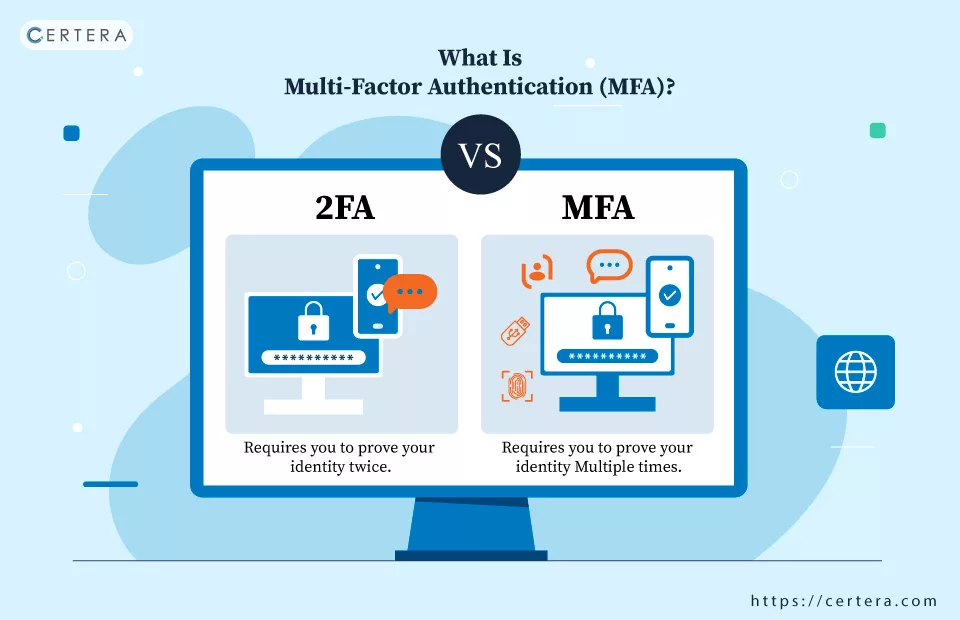
2FA vs MFA: Major Difference
As stated in the name, Two-Factor Authentication involves two factors for user identification. Here’s an instance of 2FA in action.
When a user logs in to their account with a user name, the system confirms the login credentials and prompts a second authentication factor, which could be email, SMS, or security questions. (This is 2FA!) When the verification is done, the user will granted access to their account.
Now, you must be wondering if 2FA is the same as MFA. The answer is “NO!”
So, What’s the difference? 2FA is a subset of MFA, but MFA can not be considered as 2FA. Here’s why!
- There are no pre-defined restrictions on the second-factor type in 2FA.
- All instances of 2FA are instances of MFA, but not all all instances of MFA are 2FA.
MFA is not limited to just two factors; it could be two, three, four, or even more! Simply put, MFA gives you extra layers of protection by using a mix of different checks.
Conclusion
Now that the blog is about to end, you must have understood the importance of MFA in enhancing security. Now, It’s high time to integrate this authentication method to protect your user’s privacy!
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is more secure? 2FA or MFA?
Typically, MFA is more secure than 2FA because it uses two or more authentication factors, each of which is different. This adds an additional layer of security to sensitive data, so organizations often opt for MFA instead of 2FA.
What is the difference between MFA & 2FA?
2FA requires two authentication factors for account verification, while MFA involves an additional dimension of authentication and needs two, three, or even more authentication factors.
Recommended: Understanding The Difference: Authentication vs. Authorization
