Digital Certificate vs Digital Signature: 10 Key Difference

Both digital signatures and digital certificates have major contributions to cybersecurity. Yet, both are not the same.
Concerns about cybersecurity have always circled the minds of users all over the globe. Cybersecurity uses cryptography, and digital signatures and certificates are two of the most used technologies to build a safer environment for transmitting sensitive data. However, you may be wondering about the differences between them. We have prepared this article on the differences between digital signature vs. digital certificate.
The former ensures that the document is from a legitimate organization, and the latter tells the website visitors about the organization that owns the public key. Tampered or duplicate document can compromise the data of the receiving entity. Similarly, if a website lacks a digital or SSL certificate, it can compromise the data of visitors to the site. Digital signatures and certificates are, therefore, an integral part of the cyber world.
Let’s first define what both are and then discuss the major differences between the two.
What are Digital Certificates?
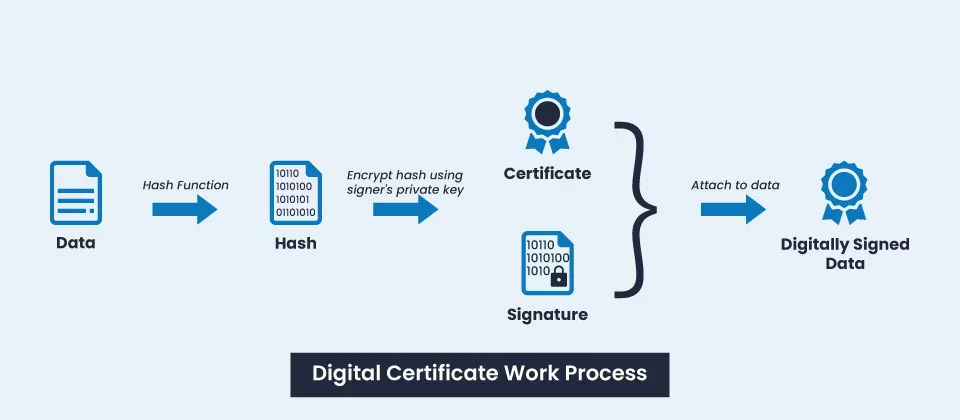
A digital certificate is a type of electronic identification that helps establish the identity of an individual, organization, or business online. In 1983, it was Invented & introduced as a secure & reliable way to verify the identity of the parties involved in digital communication.
Typically, it is made up of a public key and other identifying information like name and contact details of the certificate holder. The public key is shared with other parties to establish secure communication, and the private key is kept secret, used to decrypt messages sent to the certificate holder.
Digital certificates are widely used to secure e-commerce transactions and communications. When you visit a website that has a digital certificate, your browser can verify the authenticity of the website’s identity & ensure that your communication with the website is encrypted and secure. To put it in an easier way, a digital certificate on a website or of a business proves that they are really who they say they are, i.e., the real owners of the public and private key pair.
How to Obtain a Digital Certificate?
To obtain one, you must obtain one from a trusted certificate provider like Certera, Sectigo or Comodo, also known as a Certificate Authority (CA), who will issue the certificate after verifying your organization’s domain ownership and registration details.
To get one you must:
- Send a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) to the CA
- Verify domain ownership and the business’s registration details!
The time required to issue a digital certificate varies, with some certificate can issued within minutes, while others may take up to five days. Once you buy SSL Certificate the next step it to install it on the website to enable secure communication channel with your website visitors & display the organization’s information in the certificate details.
An SSL certificate contains the public key, private key, digital signature, organizational details, serial number, & an expiry date that is updated upon renewing the certificate. It is crucial to keep the certificate up to date to maintain secure communication channels and prevent unauthorized access.
Let’s now understand the other one, what they are, and where to utilize them.
What are Digital Signatures?
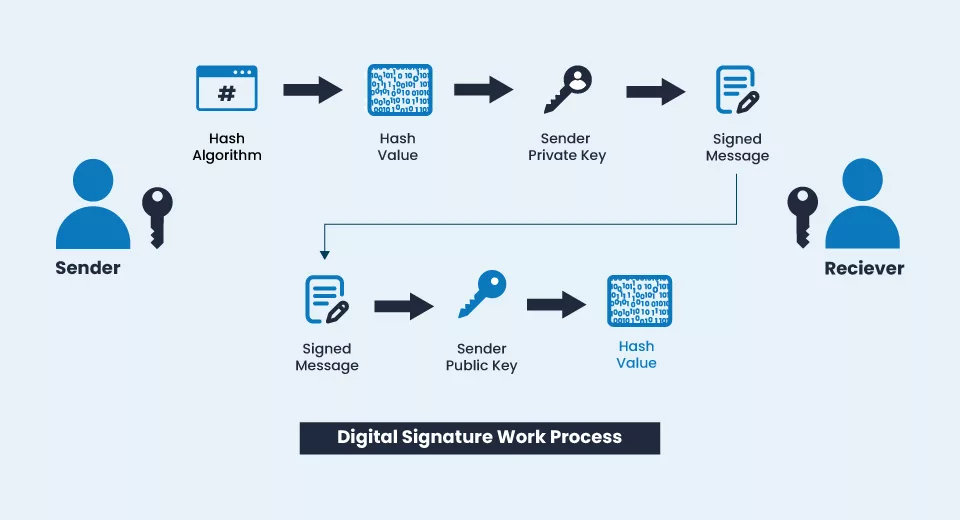
Digital Signature introduced in the year 2000 and now being used for several decades. It is a cryptographic technique used to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital software, code, or executable. It uses encryption to provide a verifiable time stamp.
With Digital Signature a signer uses its private key to create a unique digital code attached to a Document/Software. It can be verified by anyone with access to the signer’s public key. Hence, it provides a way to verify the document’s authenticity or software and prevent unauthorized modifications.
Attackers may attempt to breach a business’s database by sending modified or forged documents. The signatures prevent this by providing a way to verify the document’s authenticity. Many threat actors want to get into the database of medium or large businesses. Duplicate or bogus documents are one way to breach a business’s database. As digital signatures use public key cryptography to bind the signature to a specific entity, it allows recipients to verify the authenticity of a document as it contains company details and other confidential information.
To get one for your organization or yourself, you must approach the trusted CA and request for it.
How does a Digital Signature Work?
Once you get the signature you are allowed to sign all the documents you have created or create in future. Meaning that the document is from you, a legitimate owner of the document.
Say another enterprise wants some critical documents from you. You can sign the document with this signature, attach it to the mail, and send it to them.
By verifying your signature, the recipient can be sure that the document has not been tampered with & that it comes from a legitimate source. This provides a secure method of exchanging sensitive information online and prevents unauthorized entities from accessing your data.
In a world where most of our communication happens online, that’s how crucial these signatures are. There are differences between them, and people from cyberspace must understand those differences.
Key Differences Between Digital Signature vs. Digital Certificate
Purpose: A Digital Signature is used to verify the authenticity of a document and a Digital Certificate is used to verify the legitimacy of a business or individual
Working: The Digital Signature is used to sign a document & ensure it hasn’t been tampered with, and a digital certificate is used to encrypt data being transmitted between two entities in a secure communication channel.
Process: With a digital signature, the recipient can verify the document has not been modified since it was signed. With a digital certificate, all communication happens within an encrypted channel, & there is no need for the recipient to verify that the data hasn’t been tampered with.
Technological difference: A digital signature uses a hash-value to verify the authenticity of a document’s owner, and a digital certificate contains personal information that allows website visitors to verify the legitimacy of the website or organization.
Data Modification: Digital signatures prevents the document forgery scenario, and digital certificates help website visitors make safer online transactions and form filings by encrypting the data in real-time.
Standards: Digital Security Certificates uses public key cryptographic standards, and digital signatures use DSS (Digital Signature Standards).
Use case: Digital signature technically used to sign & verify documents sent between two devices, and digital certificates are used to establish a trust in online communications.
Boosting Trust: A digital signature brings the sender and receiver on the same page by confirming that both entities have the same document. The digital certificates make the customers entrust website owners with their crucial personal information.
Digital Signature Vs. Digital Certificates: Side by Side Comparison
| Digital Signature | Digital Certificate |
| Helps verify the document’s authenticity and the person or organization who has sent it. | Helps to understand that a CA-verified legitimate business owns the platform. |
| Makes sure that the sender or signer cannot non-repudiate the signed document | Make sure that the information shared between the client and the server remains unreadable for ill-intended third-party. |
| Used to send the document under the ownership and let the receiver know it is not tampered with. | Used to encrypt the in-transit data of the customers visiting the website on which the certificate is installed. |
| Based on DSS | Based on cryptography standards set by the internet security forum Public Key Infrastructure Working Group. |
| Timestamp is sent with the document itself. It tells the receiver about the individual’s details and when the document was signed. | The website owners can use the timestamp anywhere on their website to boost customers’ confidence. |
| Used for sharing apps and software, authorizing transactions, loan applications, and other applications where forgery might be possible. | Used for SSL encryption on websites, code signing, email encryption, IoT (Internet of Things), etc. |
Final Words
In the vast ecosystem of the Internet, security is paramount. Unfortunately, there are always sneaky predators lurking in the shadows, waiting to pounce on any vulnerability they can find. That’s where the certificates and signatures come to the rescue! These technologies are like the protective armour and shield of the digital world. Both technologies are essential in terms of providing security or stamping the authenticity of a document. With these powerful tools, you can rest easy knowing that you’re safe and sound in the digital wilderness. Let us know if you have any doubts about the difference between digital signatures vs. digital certificates.
