Mitigating the OWASP Top 10 Vulnerabilities: Strategies for Protecting Your Systems
We are in a world where the cyber environment is becoming more unpleasant and threatening; therefore, non-profit open-source organizations, such as OWASP, play a crucial role. It is completely focused and dedicated to enhancing security.
The online organization OWASP helps developers, engineers, designers, and company owners with potential risks posed by the most prevalent web application security vulnerabilities through the utilization of free and publicly accessible resources.
This article will provide a more comprehensive overview of OWASP, the top ten cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and the corresponding techniques for mitigating them.
What is OWASP?
The acronym OWASP refers to the Open Web Application Security Project. It is a non-profit organization whose primary objective is to strengthen software security through the implementation of community-developed open-source programs, the formation of local chapters throughout the globe with participants, learning and meetings, forums, and conferences.
What is OWASP Top 10?
OWASP updates and releases a list of the top 10 web application vulnerabilities periodically. Along with the OWASP Top 10 Threats, the list also discusses each vulnerability’s possible consequences and how to avoid them. A wide range of knowledgeable sources, including security consultants, designers, and security teams from businesses and organizations of all sizes, were employed to create the entire list. It is widely recognized as a fundamental manual for best practices in online application security.
In 2021, OWASP shared the list of the top 10 vulnerabilities, including three new categories, four categories with renamed and expanded scopes, and some of the top 10 category consolidation.
During the OWASP’s twentieth Anniversary on September 24, 2021, the OWASP organization released the most recent OWASP Top 10 2021. If you are familiar with the 2020 list, you’ll notice that the 2021 OWASP top ten has undergone a significant shuffle, with Broken Access Control taking the top position, replacing SQL injection.
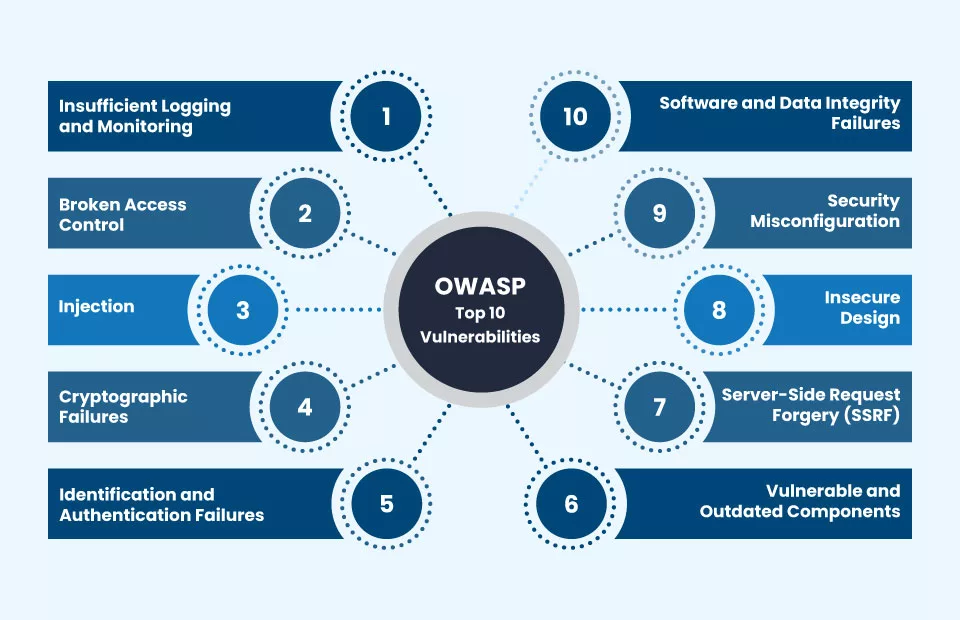
In this section, let’s explore the Top 10 OWASP vulnerabilities to understand more about their impact and corresponding prevention strategies.
- Broken Access Control
- Cryptographic Failures
- Injection
- Insecure Design
- Security Misconfiguration
- Vulnerable and Outdated Components
- Identification and Authentication Failures
- Software and Data Integrity Failures
- Insufficient Logging and Monitoring
- Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
1. Broken Access Control
Broken access control is a lack of adequate authentication checks for users attempting to access restricted resources. This vulnerability can occur when an application or system fails to implement proper access restrictions, such as passwords, user roles, or permissions.
Examples include the absence of authorization restrictions, evading access control measures, incorrectly configuring access control policies, and granting people access to system files or databases without the appropriate authorizations.
Broken access control can have serious repercussions, including data breaches, identity theft, fraud, and compliance issues.
Mitigation Methods for Broken Access Controls
There are several solutions to fix the broken access control vulnerability:
- RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) was one of the most significant methods for managing access and permissions in your system. It allows you to give roles to users and controls the features and data to which every role has access.
- Accounts that aren’t used or active enough should be deleted.
- Use trustworthy and secure authentication methods. Use various authentication methods, including biometric authentication, OTP (one-time password), and multi-factor authentication.
- To ensure security, you must encrypt data when storing it (at rest) and transmitting it (in transit).
- Disable any additional access points that aren’t needed right now if there are any.
- Monitoring and auditing access logs regularly can help you identify any unusual behavior and swiftly address any issues that arise.
- You can deal with any evolving hazards and vulnerabilities by continuously updating access procedures and regulations.
2. Cryptographic Failures
It is a critical web application security vulnerability. Data contain sensitive information that requires additional security, whether it is at rest or in transport. Companies governed by regulations like CCPA, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, etc., must consider this extremely crucial.
Utilization of outdated padding techniques, insufficient randomization for cryptographic processes, vulnerable side-channel data or cryptographic warnings, storing information in plaintext, failure to utilize effective and recent encryption algorithms, erroneous management of keys, etc., are a few examples of cryptographic failures.
Mitigation Methods for Cryptographic Failures
- Remove caching for responses containing sensitive information
- Use current and verified cryptographic protocols, activities, and algorithms.
- Typically, using digital signatures verifies the sender’s identity and assures data accuracy. Commonly employed digital signature methods include HMAC, DSA, and RSA Signatures.
- Minimize/reduce the data surface area’s size.
- To ensure security, you must encrypt data both when storing it (at rest) and when transmitting it (in transit).
- When saving passwords, use strong adaptive and salted hashing functions.
- Regular vulnerability assessments and cryptographic system audits might help discover vulnerabilities and ensure prompt remediation.
3. Injection
An attacker can potentially exploit injection vulnerabilities when injecting unauthorized data into the interpreter via SQL, NoSQL, OS, or LDAP. This attack vector allows for the malicious injection of data to deceive the interpreter and force the application to perform unintended actions, such as executing unexpected commands or gaining unauthorized access to data.
Injection attacks could impact any application that takes parameters as input. The extent of the application’s input validation controls closely correlates with the possible threat level. Unauthorized access to data, damage to integrity and confidentiality, as well as compromised system functionality can occur from this kind of activity.
Mitigation Methods for Injection
- SQL injections, XSS, and other types of injections are some instances.
- Before running any user input against a database or other backend components, make sure to validate and sanitize it.
- To further regulate and restrict the capacity of attackers to exploit SQL injection vulnerabilities, organizations might limit the code accessible to a database.
- Database administrators should enforce prepared statements and parameterization, employ stored procedures, whitelist user inputs, and minimize functionality.
- Remove the interpreter completely using a secure API.
- Apply efficient server-side validation and an intrusion detection method that identifies unreliable client-side behaviors.
4. Insecure Design
When a design or architectural defect leads to a vulnerability that a malicious attacker may use, it is referred to as insecure design in online applications. This scenario can be normally called a Missing or inadequate/poor control design.
This vulnerability category, comprising almost 262,000 occurrences, focuses on the dangers connected to weaknesses in an application’s architecture. An ideal implementation will not be able to rectify insecure designs. Why? To reduce the risks, they need security controls. Insecure configuration can adversely impact individuals or organizations by causing losses in money and reputation. Systems and applications with insecure configurations are especially vulnerable to security threats, including unauthorized access, denial of service, and data breaches.
Mitigation Methods for Insecure Design
- Distinguish between system and network layers tiers based on the requirement for visibility and protection.
- Reduce resource use by users and services.
- Develop and employ a secure development lifecycle with AppSec experts to assist in analyzing and creating security- and privacy-related measures.
- Create a library of readily available secure design patterns or modules.
- For significant transactions, access control, business logic, and authentication, use threat modeling.
- Updating security patches for software can assist in preventing these vulnerabilities.
To protect your data against growing security risks, keeping up to date with the latest security mitigation methods and trends is of utmost importance. Since researchers constantly discover new vulnerabilities.
5. Security Misconfiguration
Any security control that is improperly configured, insecure, or inadequately written is a security misconfiguration. Examples of this include insecure applications, incorrect technical communications, and incorrect modifications in software configuration. This category, which comprises twenty-eight thousand CWE occurrences, is an immediate consequence of the recent transition to highly customizable software. However, the more flexibility you must configure your software, the simpler it is to make errors.
According to OWASP’s top 10 2022 statistics, misconfigurations are considered one of the primary triggers for the listed vulnerabilities. This vulnerability is particularly widespread and frequent within the OWASP top 10 vulnerabilities. Several misconfigurations provoked the organization in grave danger for cybersecurity, including considering insecure default settings into account, excessively affordable cloud storage services, incomplete or outdated configurations, etc,
Mitigation Methods for Security Misconfiguration
- Use a process of security strengthening to protect your systems. Create and automate a method for deploying a secure, distinct environment with the identical configuration as the original but with different login credentials.
- Using a minimal platform is sometimes preferable. Ignore any unwanted alarms, services, and functionalities.
- Include an activity requiring you to re-evaluate and regularly adjust the configurations for patches, updates, and cloud storage privileges in your patch management process.
6. Vulnerable and Outdated Components
Software frameworks or components that contain vulnerabilities or are no longer providers are referred to as “vulnerable and out-of-date components” and consequently open to attack.
Many contemporary distributed web applications use open-source libraries and frameworks as part of their design. Any part that has a known vulnerability develops into a weak point that can compromise the security of the entire application.
While the use of open-source components with known vulnerabilities is ranked low in terms of the complexity of security issues, it occupies the top position in the OWASP Top 10 list when it comes to the frequency of vulnerabilities leading to authenticated information breaches. This category has recorded over 30,000 incidents in recent years.
Mitigation Methods for Vulnerable and Outdated Components
- Updating all software components, including third-party libraries, to the most recent security fixes and patches is recommended. You should check for security updates frequently and install them as soon as they become available.
- To ensure that all requirements are monitored and kept up-to-date, utilize a trusted dependency management solution. This may assist in promptly identifying insecure and out-of-date components and replacing them with more secure ones.
- Address configuration management for all components incorporated into the organization’s frameworks.
- A robust vulnerability database that has been updated with threat intelligence data should be used for scanning.
- Automate patch management procedures as much as possible to minimize operational risks associated with patching. This includes automating selecting, testing, and delivering appropriate patches.
7. Identification and Authentication Failures
Cybercriminals can be capable of stealing and misusing login credentials, private keys, or session credentials and temporarily or permanently mimic other individuals’ true identities and privileges if apps handle session management or user authentication incorrectly. The vulnerability seriously compromises the security of the application and the resources it accesses, and it additionally poses a serious risk to other network-connected resources and devices in the network.
Inadequate password management, automated or brute force attacks, improper access control, and user interactions can lead to potential authentication and identification failure risks. These risks may include reused or publicly accessible sessions after logging in.
Mitigation Methods for Identification and Authentication Failures
- Practice multi-factor authentication
- Never use the default credentials when installing, especially for administrators.
- Install a secure sessions manager that produced session IDs with a time restriction.
- Keep track of unsuccessful login attempts and place restrictions and time limitations on them.
- Maximize the procedures involved in credential recovery, registration, and other aspects of authentication.
- Implement reliable and secure password managers.
8. Software and Data Integrity Failures
Software and data integrity problems occur when infrastructure and code do not have protection from data security breaches. Untrusted sources, repositories, or content delivery networks (CDNs) are examples of apps that utilize plugins, libraries, or modules. The potential risks of an unprotected pipeline can involve unauthorized access, malicious code, and system compromise.
A lot of applications nowadays include automatic updates features that enable updates to be downloaded without the need for integrity checks and applied to previously trusted apps. With this functionality, hackers could have the opportunity able to launch and distribute their updates throughout all systems.
Mitigation of Software and Data Integrity Failures
- Use a digital signature or any other similar technology to verify the authenticity of applications, information, and programs as well as their source.
- Verify the CI/CD pipeline’s integrity by implementing strict restrictions on access, appropriate configuration, and necessary data segregation.
- Regular software and system updates will ensure that software and hardware are updated with the most recent security patches and fixes for issues. This may minimize the possibility of confidentiality issues carried on outdated applications.
- Data validation techniques will help in ensuring the data uploaded to the system is true and correct. This might involve verifying inputs, comparing data with predetermined company regulations, cleaning up data, and upholding standards for data quality.
- Examine the source code and configurations constantly for modifications.
- Verify to see if libraries and dependencies, such as Maven or npm, employ trustworthy repositories. If your risk profile is greater, examine hosting an internal, authorized known-good source.
9. Insufficient Logging and Monitoring
The application’s weaknesses in identifying and reacting to security issues are the primary concern of this OWASP Top 10 vulnerability for 2021. Attackers have an adequate chance to carry out their strategies given that the standard time frame from attack-to-attack identification is 197 days. During this timeframe, cybercriminals have plenty of time to cause damage to servers, modify databases, steal private information, and insert harmful code.
Mitigation of Insufficient Logging and Monitoring
- Employ readily accessible logging and auditing tools to identify unusual activity quickly.
- Make sure that the records are contextual and accessible in forms that allow forensic research and analysis.
- Implement security measures that prevent the manipulation of log data.
- Develop an approach for incident handling and recovery.
10. Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
Another recent addition. A web security issue known as server-side request forgery (also known as SSRF) enables an attacker to convince a server-side application to submit HTTP requests to any domain of their selection. OWASP compiled this issue from the top 10 community survey responses. Server-side request forgery is the final one of the top 10 OWASP vulnerabilities for 2021, with considerably more than 9,000 instances.
Due to this vulnerability, users can obtain information from remote resources through client-provided, unreliable URLs. If unvalidated user inputs are received, even servers protected by firewalls or Virtual private networks are vulnerable to these risks.
Mitigation of Server-Side Request Forgery
- Mandate proper verification and sanitization of input from users
- Functionalities for remote resource access, if any, must be differentiated in their impact.
- Using reject-by-default firewall procedures, prevent incoming traffic that is not legitimate.
- Don’t provide clients with poor responses.
Conclusion
A web app vulnerability may cost you and the organization a lot of money and damage the reputation of your company. Even though applications are getting more secure, hackers continue to discover new vulnerabilities.
It’s an advancement in the right direction toward protecting your web apps to go through the OWASP vulnerabilities report and understand how to avoid specific vulnerabilities. Organizations can use the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities as a reference to understand and protect themselves against the most prevalent risks and vulnerabilities in their apps. Companies can reduce their risk of security breaches and minimize the effect of upcoming attacks by being mindful and strongly resolving these weaknesses.
It will always be a tug-of-war in the end. But your apps will already be more secure if you maintain a watchful eye on the top 10 vulnerabilities and understand how to fix them.
Level up your security immediately!
FAQ’s
1. What are the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities?
- Injection
- Broken Authentication
- Sensitive Data Exposure
- Insecure Design
- Broken Access Control
- Security Misconfiguration
- Cross-Site Scripting
- Insecure Deserialization
- Insufficient Logging and Monitoring
- Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
2. What is the OWASP Top 10 list best used as?
A typical resource for developers and online application security is the OWASP Top 10. It illustrates a broader understanding of the most important security threats to online applications. It is globally acknowledged as the initial step towards better secure code by developers.
3. What are the 4 main types of vulnerability?
Network vulnerabilities, operating system vulnerabilities, process (or procedural) vulnerabilities, and human vulnerabilities are the four primary categories of vulnerabilities in information security.
4. What is the purpose of OWASP?
To assist website owners and security professionals in defending online applications from cyberattacks, the Open Online Web Application Security Project was founded as a non-profit in 2001. Thirty thousand volunteers work with OWASP as researchers and security analysts throughout the globe.
5. What vulnerability mitigation measures are there?
By placing internal controls into effect that decrease the attack surface of your systems, you can reduce vulnerabilities. Threat intelligence, entity behavior analysis, and intrusion detection and prevention are some examples of vulnerability mitigation.
