How to Disable HSTS in Chrome & Firefox?

Web designers, web developers, website owners, and visitors all embrace HSTS eagerly because it provides them with the desired security for their sites.
HSTS stands for HTTP Strict Transport Security. It can boost the internet by providing an additional degree of protection. HSTS protects internet connections from dangerous cyber criminals and prevents them from exposing, leaking, or compromising data.
However, HSTS has one big drawback. Its implementation causes browser issues regularly. But worry not because fixing this problem is not as challenging as you imagine.
This article will explain how to clear HSTS settings in Chrome and Firefox.
But, before we get into the fixes, let us explain what exactly HSTS is, what is the HSTS significance in the modern digital age, and What causes HSTS errors in popular browsers.
What is HSTS?
HSTS allows browsers to create stronger HTTPS connections while simultaneously restricting HTTP connections, which are inherently less secure. HSTS is useful because it stops cookie hijacking and protocol downgrade interference.
Its primary benefits are preventing attacks such as Man-In-The-Middle attacks, eavesdropping, cookie hijacking, and HTTP downgrade interference attacks.
Developers created HSTS in response to the increase in SSL Strip attacks, which could interfere with HTTPS connections and cause them to be downgraded to more vulnerable HTTP connections. HSTS acts as a security measure by transmitting a policy to the header of a web page. When a user accesses a website, HSTS forces the browser to establish a secure HTTPS connection.
However, HSTS installation might cause interruptions at times, causing browsers to display HSTS errors
Examples:
- Your Connection is Not Private
- Security risk ahead
- NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID
- SSL/TLS Handshake Failed
When you access the page in another browser, the error may not appear, indicating that your HSTS settings are triggering a problem.
Benefits of adopting HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)
- Improved website security
- Prevents Mixed-Content Errors
- Increases User Trust
- Avoids URL Hijacking
- Improves Website Performance
Improved Website Security
By encrypting all communication between a user’s browser and a website, HSTS ensures a reduced risk of man-in-the-middle attacks and other security concerns.
Prevents Mixed-Content Errors
Using HSTS prevents browsers from accessing non-HTTPS content, which is crucial in preventing mixed-content problems and boosting website security.
Increases User Trust
HSTS indicates that your website considers security seriously and may assist in building user trust and credibility.
Avoids URL Hijacking
HSTS helps prevent attackers from stealing your website’s URL.
Improves Website Performance
HSTS can enhance website performance by removing the need to frequently redirect visitors from HTTP to HTTPS, boosting page load times, and lowering server load.
What causes the HSTS errors in popular browsers?
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) problems in popular browsers may occur for multiple reasons the certificate is expired or invalid, the server configuration is not properly implemented, the DNS issue is not fixed, etc. Let’s see these reasons one by one.
- Expired Certificates
- Invalid Certificates
- Invalid Server Configurations
- DNS Issues
- Third-party Software Interference
Expired Certificates
If a website’s SSL certificate expires, users may get an HSTS error warning message while attempting to access it.
Invalid Certificates
If the SSL certificate is not issued by a trustworthy Certificate Authority (CA), browsers may be unable to validate it, resulting in HSTS errors.
Invalid Server Configurations
When attempting to connect to a website server that is not properly configured to accept HTTPS traffic, users may receive an HSTS error or warning message.
DNS issues
Users can get an HSTS error while attempting to access a website if there are DNS issues or the domain name is not properly configured.
Third-party Software Interference
Some security applications and browser extensions can interfere with the HSTS protocol and cause issues.
All communications between the user and the website will be in plaintext if you use HTTP instead of HTTPS; this implies that hackers can take a wide range of sensitive information from you, including Financial information, social security numbers, payment card numbers, phone number, health information, physical address, and login credentials.
How can I remove or disable HSTS in different browsers?
Here’s a common scenario that could have you questioning yourself for a while: You’re attempting to access a website when you see the warning,
- Your connection is not private
- Security risk ahead
If you receive this strange notification, try using a different browser to see if you can access the page without receiving the same message. If you can, it suggests that there is most likely a problem with the original browser’s HSTS settings.
You then have a choice that you can clear the HSTS settings or disable HSTS on your web browser.
Clearing HSTS Settings in Chrome
When there is a problem with your HSTS settings in Chrome, you will usually see an error message like “Your connection is not private.” This error message’s advanced menu would almost certainly include a clear mention of HSTS settings. You can disable HSTS in Chrome by following the steps provided below:
Process:
- Open Chrome.
- Type “chrome://net-internals/#hsts” in the address bar.
- In “Query HSTS/PKP domain,”; enter the domain name of the site for which the HSTS settings are to be removed.
- Finally, enter the domain name under this Delete domain security policy and click the Delete button.
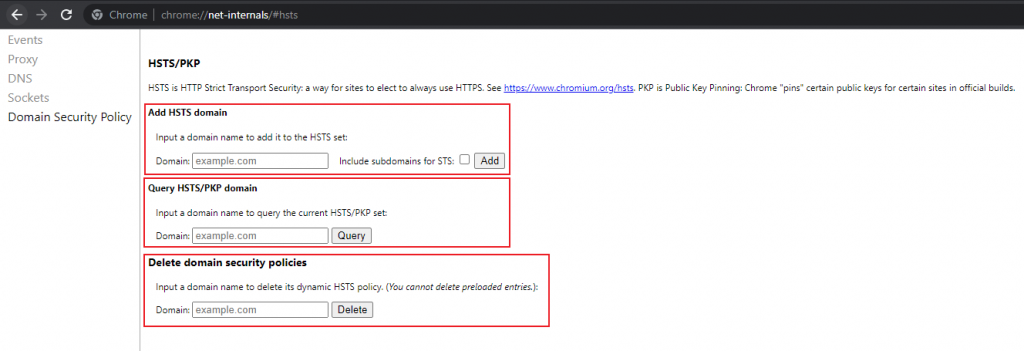
HSTS settings are cleared in Chrome.
Clearing HSTS Settings in Firefox
While to disable HSTS in Firefox, there are various techniques available; the simplest is as follows:
- Begin by closing any currently open windows.
- Then, press Ctrl + Shift + H to see your internet history.
- Navigate to the site where you want to delete the HSTS settings.
- Right-click the website and select Forget About This Site. Keep in mind that this will delete all data from the site that is currently open in Firefox.
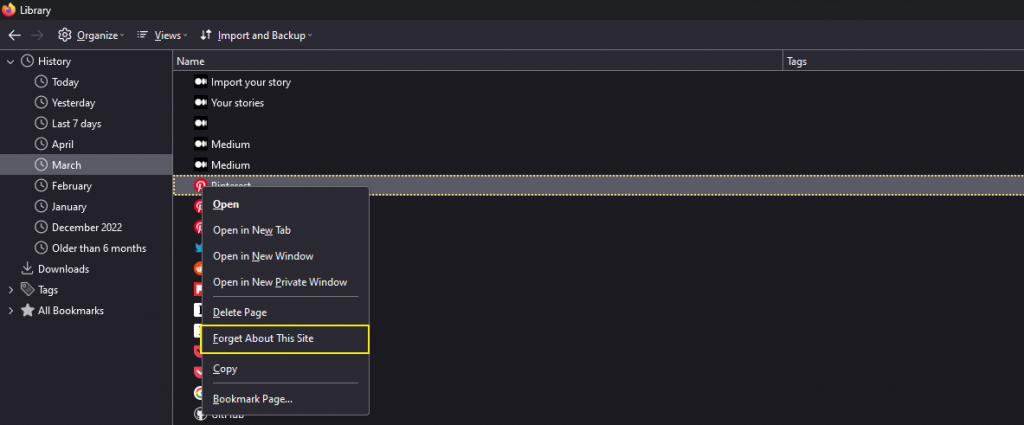
That’s it! Firefox’s HSTS settings have now been cleared.
Wrap up:
As you’ve noticed, HSTS settings strengthen the security of your website. If you’re creating your website, it’s highly advised that you use HSTS to improve your online security. Before you begin using HSTS, keep in mind that you must first install an authorized and trustworthy SSL Certificate.
Ensure that you have an SSL certificate from Certera (a reputable SSL certificate vendor) installed. The same is configured properly before using HSTS settings to eliminate the possibility of errors.
As a website visitor, you may easily disable HSTS settings on your selected website. However, we urge you to avoid sending crucial information on such HTTP sites.
HSTS has multiple benefits over the small browser errors that are occasionally displayed. While HSTS has numerous positive effects, random browser errors might be a drawback. If this happens, clearing and disabling HSTS is a simple process. After that, you may go back to business and enjoy an uninterrupted browsing experience. So, utilize HSTS to protect your website from a wide range of cyber threats.
FAQ’s
How do I turn off HSTS in Chrome?
- Open the Google Admin console.
- Navigate to the Menu > Devices > Chrome > Settings > Users & Browsers.
- Scroll down to Network settings and look for the HSTS policy bypassing list.
- Enter the list of hostnames that are not subject to the HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) policy check.
- Save it.
How do I fix the HSTS error in Firefox?
Steps for Clearing HSTS Settings in Mozilla Firefox:
- Right-click the site and choose Forget About This Site. Please remember that this will delete all data from the page presently open in Firefox.
- Restart the browser, and the issue should be fixed.
Why is Chrome preventing access to websites? HSTS?
HSTS is a web security policy technique that requires web browsers to interact with websites exclusively over secure HTTPS connections (and never HTTP). It helps in the prevention of protocol downgrade attacks as well as cookie hijacking.
Is HSTS turned on by default?
Optional Boolean attribute. Specifies whether HSTS for a site is enabled (true) or disabled (false). When IIS responds to an HTTPS request, the Strict-Transport-Security HTTP response header is inserted if HSTS is enabled. The default value is false.
