What is a Cipher? Types of Ciphers in Cryptography

Ciphers are often grouped based on their operation and how their key is applied to encryption and decryption. Block ciphers combine symbols into a fixed-size message (the block), whereas stream ciphers use a continuous stream of symbols.
The same key is used for encryption and decryption when utilizing a symmetric critical method or cipher. Asymmetric vital algorithms or ciphers employ a different key for encryption and decryption.
Are you looking into ciphers? Then you have come to the correct location. This blog covers almost all types of ciphers in cryptography.
What is Cipher?
- The cipher algorithm is commonly used in cryptology, a field dealing with the study of cryptographic algorithms. This technique is used to encrypt and decrypt data.
- The secret or symmetric key encryption will depend on the symmetrical cipher used.
- The same cipher and encryption key are used in the same manner by the symmetric method to encrypt and decrypt the data.
- Symmetric key encryption, often known as secret key encryption, is built on symmetric ciphers.
- It can be a goal to convert plain text to ciphertext or vice versa.
- Ciphers change data by converting letters or other plaintext into ciphertext. The ciphertext should be presented in the form of random data.
- By analyzing the original and plaintext data, the cipher creates a ciphertext that seems to be random data.
- No matter whether the goal is to convert plaintext into ciphertext or ciphertext into plaintext, the same encryption key is used to encrypt data in the same way, utilizing symmetric encryption techniques.
- The ciphertext refers to the data generated through any technique.
- Modern cipher techniques enable network traffic encryption using private communication in a number of networking protocols, including TLS, or transport layer security.
- Many communication systems, like digital televisions, mobile devices, and ATMs, employ ciphers to provide security and privacy.
How Does a Cipher Work?
- Ciphers use an encryption method to change plaintext, a readable communication, into ciphertext, which appears to be a random string of letters.
- Ciphers are also called stream ciphers since they can encrypt or decrypt bits in a stream.
- They can also use block ciphers, which break up ciphertext into uniform units of a predefined number of bits.
- Modern cipher implementations change data as it is encrypted using the encryption method and a secret key.
- Ciphers more resist brute-force attacks when their keys are longer (measured in bits).
- Depending on the algorithm and use case, professionals recommend that current ciphers be designed with at least 128 bits or more, even if the key length is not necessarily connected with cipher strength.
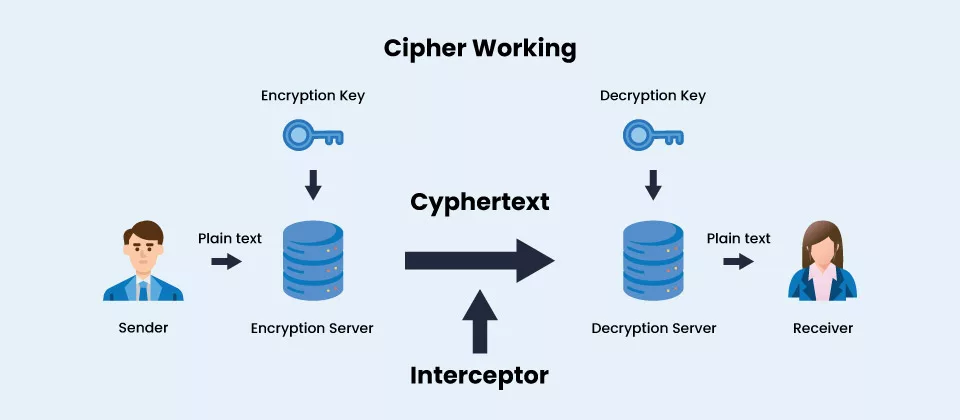
- Because a key is such a vital component of an encryption process, the key is maintained as a secret rather than a procedure in real-world ciphering.
- Even if someone is familiar with the procedure, a robust encryption mechanism should make reading the ciphertext with the necessary key easier.
- As a result, a cipher requires the possession of a key or set of keys by both the sender and the recipient to work.
- The same key is employed in symmetric essential data encryption and decryption techniques.
- Asymmetric key algorithms encrypt and decrypt data using public and private keys.
- Asymmetric public key cryptography, commonly known as asymmetric encryption, uses large integers that have been paired but are not equal.
Following is a snapshot of a key pair:
- The public key is accessible to everyone.
- The secret key sometimes called the private key, is kept hidden.
- A message can be encrypted with any key and decoded using the opposite key that was used to encrypt it.
- The public key is used to encrypt messages that can only be read by the private key owner, even if the key pair only uses the private or secret key to encrypt or decrypt data.
Why are Ciphers important?
By converting messages into a format that is unreadable or unintelligible to unauthorized parties, ciphers guarantee the confidentiality and integrity of communications.
Information and data are encrypted using ciphers so only those with the proper key or password can see it.
Additionally, ciphers are utilized for message verification, digital signatures, and authentication. Using ciphers can guard against data theft, eavesdropping, and hacking attempts and secure sensitive information.
Symmetric ciphers are the most used ones for protecting internet communication. Additionally, they are included in several protocols for data-sharing networks.
In particular, when combined with HTTP Secure (HTTPS), TLS and Secure Sockets Layer use ciphers to encrypt data at the application layer.
Virtual private networks that connect employees in remote or branch offices to corporate networks utilize protocols that encrypt data transmission using symmetric vital methodologies.
Symmetric ciphers are frequently employed in wireless Internet networks, e-commerce, banking websites, and mobile phone services to protect user data privacy,
Several protocols use asymmetric cryptography to authenticate and encrypt endpoints.
It also protects the transfer of symmetric keys used for session data encryption. These standards comprise the following:
- HTTP
- Secure Shell
- Open Pretty Good Privacy
- TLS
- Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions
Types of Ciphers in Cryptography
There are several methods to categorize ciphers, including the following:
Ciphers can be categorized using a variety of techniques, such as the ones listed below:
Block Ciphers
Data is encrypted in equal-sized blocks using Block ciphers.
Block ciphers are symmetric vital algorithms that work with fixed-length data blocks to produce encrypted results. The data is encrypted and decrypted using a fixed-length key.
The input data is separated into equal-sized blocks, and the algorithm uses the same key for all the blocks to operate independently on each block. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Triple DES (3DES), and Data Encryption Standard (DES) are a few examples of block cipher.
Stream Ciphers
Data streams often received and sent across a network can be encrypted using Stream ciphers.
On the other hand, the symmetric vital techniques used by stream ciphers encrypt and decode data one bit or byte at a time. They create a keystream, which is used to encrypt and decrypt the data using a key and an initialization vector (IV).
The encrypted output is created by combining the keystream with the plaintext using an XOR technique. Applications where data is sent in real-time, such as video and audio communication, frequently use stream ciphers. The stream ciphers RC4, and Salsa20 are a couple of examples.
Caesar Cipher
Julius Caesar is believed to have used this cipher to travel securely with his men.
In this simple substitution cipher, each letter of the plaintext is relocated a predetermined number of places down the alphabet. Caesar is alleged to have worked three shifts.
Substitution ciphers are typically implemented by writing down the plaintext alphabet, followed by the ciphertext alphabet, shifted by the number decided upon by the participants. A three-letter shift puts the letter D over the plaintext letter A, E over B, etc. The number of characters shifted is a basic form of a key.
Atbash
With this encryption, the plaintext alphabet is projected back onto itself as a replacement cipher.
The plaintext letters A through C are converted into the ciphertexts Z through Y, respectively. The names of Atbash are taken from the first and last letters of the Hebrew alphabet. Hundreds of years have passed since it hadn’t been utilized.
Simple Substitution Cipher
This one has also been in use for a very long time. It creates a 26-character key by substituting a new ciphertext character for each plaintext letter.
In contrast to the Caesar cipher, the enciphering alphabet is mixed up instead of only being shifted a specific number of times.
Playfair Cipher
Instead of using single letters as in a basic substitution cipher, pairs of letters are encrypted in this approach.
A key table is first created in the Playfair cipher. The plaintext is encrypted using the key table, a 55-grid of alphabets. One letter of the alphabet (often J) is left off the table because we only need 25 rather than 26, and each of the 25 must be distinct. J is changed to I if it is found in the plaintext.
Vigenère
This polyalphabetic substitution cipher, which uses several alternative alphabets, suggests that it is based on substitution. Caesar ciphers based on a keyword’s letters are used as part of the Vigenère encryption in a sequence of interconnected patterns.
The Vigenère square or table is used to jumble up the source material.
Enigma Cipher
The Germans used a sophisticated cipher system in World War II. After scrubbing input plaintext, it used several revolving wheels, connectors, and wires to encrypt the output. The key to this cipher was the original alignment of the wheels and plugboard structure.
One Time Pad Cipher
One Time Pad Cipher is an unbreakable cipher that encrypts and decrypts communications using a random key called the one-time pad. The key is never reused and is as long as the message is encrypted. The key is a “one-time pad” since it can only be used once.
Wrap up!
In conclusion, ciphers are a crucial type of encryption for securing private data. The security of the key is the core of every cipher, even though several ciphers have been developed over time, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages. We expect the development of increasingly more sophisticated encryption methods as technology advances.
FAQ’s
What are the different types of ciphers in cryptography?
- Block ciphers
- Stream Ciphers
- Substitution ciphers
- Transposition ciphers
- One Time Pad Cipher etc.
What is the difference between Ciphers and Cryptography?
It is the process of turning ordinary text into a cipher that requires a key to decipher. Security of a message through encryption and decryption is defined as cryptography.
The use of cryptography is known as encryption. It is the skill of creating codes using encryption and decryption techniques.
What are the four basic types of encryption systems?
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
- Blowfish.
- Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA)
- Triple DES.
Which is the More Secure Cipher?
AES Encryption
Governments, security agencies, and regular companies use the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), one of the most secure encryption forms, for sensitive communications. “AES uses symmetric” key encryption.
What is a Cipher in Cryptography?
Systems for encrypting and decrypting data are called ciphers, often known as encryption algorithms. A cipher uses a key to reveal the process by which it transforms the original message, known as plaintext, into ciphertext.
