What is a S/MIME Certificate and How Does It Work?

You might be thinking, “What is S/MIME?” Please don’t be alarmed; you are not alone if you were concerned after reading the title. However, most internet users have sent emails using S/MIME encryption certificates several times. If they use a corporate email account, S/MIME (often spelled “SMIME”) is not a term most internet users are familiar with.
Continue reading for more information about S/MIME, including what it is, how it works, and how to use it to secure your emails.
What exactly is S/MIME?
S/MIME is abbreviated as Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension. S/MIME certificates are frequently called personal authentication certificates or email signing certificates.
In essence, this email security protocol works in two ways.
- To assist the email receiver in verifying the sender’s legitimacy.
- The email’s contents are being read, altered, intercepted, or compromised by unauthorized individuals, whether at rest or in transit.
Since these were introduced, S/MIME certificates have effectively solved security concerns and weaknesses. S/MIME certificates have developed and become impenetrable over time to solve security vulnerabilities like EFAIL (a vulnerability that impacts end-to-end encryption systems).
S/MIME is specified as a technology that is frequently employed by organizations to improve email security. It offers encryption, which shields the content of email messages from unauthorized access. It also has digital signatures, which make it an effective defense against many email-based incidents by verifying that you are the message’s legitimate sender.
In simple terms, S/MIME is a widely used protocol that uses S/MIME certificates to enable the sending of encrypted and digitally signed email messages.
Why S/MIME Certificate is Necessary?
Over the past two decades, emails have replaced phone conversations as the primary business and official communication method.
According to Statista’s research, 4.03 billion people used email in 2021, and 4.48 billion are expected to do so by 2024.
Every day, millions of emails are sent and received between various devices, making it necessary to secure these communications. Due to the quantity and kind of sensitive data, the significance is rapidly increased in a commercial business.
Suppose you maintain sensitive Information such as Personal employee data, Information about credit and debit cards, customer details, and contact info. In that case, you must consider encrypting communication and securing sensitive Information. You have to protect against cybercriminals compromising the data and anyone tapping your emails. These individuals are well known for being skilled at utilizing your email and developing phishing attacks to deceive people into disclosing personal Information.
According to FBI statistics, email account breaches and business email intrusions involving these criminals resulted in a loss of USD 26 billion between FY 2016 and FY 2019.
We’ll offer a few reasons why you need S/MIME to secure your emails if you still need convincing about using ultra-secure certificates anywhere that will allow them.
- S/MIME Prevents Phishing Attacks
- S/MIME Enables Secure and Encrypted Communication.
Recommended: What is Email Spoofing? Definition, Example & Prevention
How Is My Email Encrypted With S/MIME?
Now that you know what S/MIME is and what it is used for, you will see “What is the S/MIME encryption process?”
S/MIME works through public and private keys that relate mathematically. Asymmetric cryptography is the foundation of this technology. Even if you know the public key, it is challenging to determine the private key. If you use this technology to encrypt, your emails will be encrypted using the recipient’s public key. It is only possible to decode the email with the associated private key.
The person who will have the private key is the email’s intended receiver. You cannot transmit emails or attachments containing sensitive information to anyone other than the designated recipient. Hackers or other individuals cannot access the email you send unless the private key is compromised.
You can sign emails with S/MIME to show that you are the email’s authorized sender. It does not mean your emails to be manually signed with a pen when we say you can. Your emails will be digitally signed using this technology. Your distinctive Digital Signature will be applied to the email you send using the private key allocated to it.
Every time you send an email, this will be carried out. Whenever the receiver opens the email you sent, the public key will validate your signature. This signature can verify your identity and assure the receiver that you are the email’s authentic sender.
You might need clarification as to why you must sign your emails. Securely sending sensitive information online through email is necessary due to increased phishing emails and online crimes.
Ensuring your emails do not get into an unauthorized hand is of the utmost significance since it is becoming harder to distinguish between bogus and authentic emails. Verifying the senders of emails is crucial due to the rise in phishing attacks. It is prudent to utilize S/MIME considering the security features a S/MIME certificate provides.
Now that you understand that S/MIME certificates protect emails using asymmetric encryption, let’s explore how a S/MIME certificate works.
How Does a S/MIME Certificate Work?
S/MIME certificates utilize asymmetric encryption to encrypt email securely. You must secure an email you send to colleagues/friends to ensure no one else can view it. You can utilize a public key to encrypt your email and keep it resistant to modification and hacking.
This public key is accessible to everyone, not just the colleague you send the secure email. The email’s contents, however, are only accessible to you and your colleague without the private key. Your colleague is the only (intended) individual with access to the private key to decode and read the email. This is the way a S/MIME certificate works.
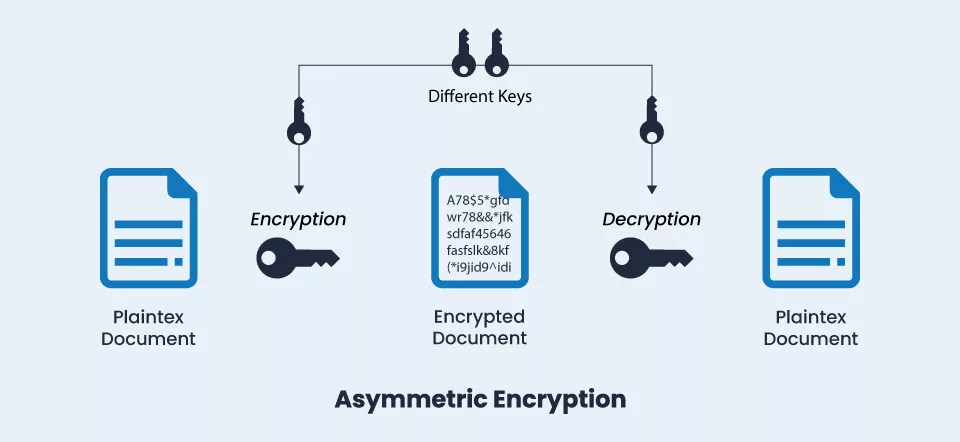
An email signing certificate, which you can get from a CA, is required to sign and encrypt your emails. To digitally sign your emails, use this certificate. The certificate you purchase will instantly be added to your email when you do so.
The public key is utilized for authentication, whereas the private key generates the digital signature. Two keys are linked to the digital signature: the public and private. The email’s digital signature shows that it was sent without modification and that the intended receiver is the only one who can access it.
How to Configure S/MIME for Windows?
We can assist you in configuring S/MIME for Windows OS, even if S/MIME deployment seems challenging.
Prerequisites
- Exchange accounts (both on-premises and Exchange Online) have S/MIME enabled. S/MIME signing and encryption cannot be used with a personal account like Outlook.com.
- Legitimate Personal Information Exchange (PFX) certificates are installed on the device.
Select S/MIME Settings
- Perform the following steps: (Insert selected certificate)
- Open the Mail app.
- Navigate to Settings > Email Security.
- In the account section, choose the account you want to configure S/MIME options.
- Select a certificate for encryption and digital signatures.
- To allow the app to select the certificate, select Automatically.
- Choose Manually to select the certificate from the device’s list of valid certificates.
- (Optional) Choose To automatically digitally sign or encrypt all outgoing messages, choose either always sign using S/MIME, always encrypt with S/MIME, or both.
- Click the back arrow.
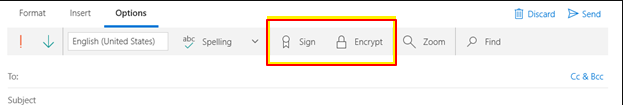
Sign or Encrypt Every Message Individually
- Choose Options from the ribbon when composing a message.
- Use the Sign and Encrypt icons to enable digital signature and encryption for this message.
Read Communications that are Signed or Encrypted
The mail application determines if a certificate is available on the system when you receive an encrypted message. When you open the mail, the message is automatically decrypted if a certificate is available.
You will be asked to insert the smart card to view the message if your certificate is stored on one. For access to the certificate, your smartcard might additionally need a PIN.
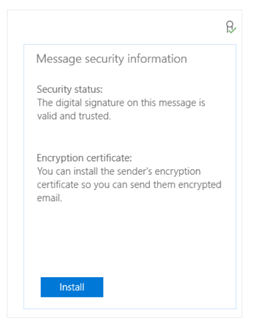
Install Certificates using a Message that was Received
If an appropriate encryption certificate is available when you get a signed email, the app provides a tool to install it on your device. Emails that are encrypted and addressed to this individual can be sent using this certificate.
- Open a signed email.
- In the reading pane, choose the digital signature icon.
- Click on Install
Features of S/MIME Certificates
You can use several cryptographic security features when utilizing S/MIME certificates for email applications.
Message Integrity:
This ensures that the message’s data and all its contents are not changed. The message’s authenticity must be protected. Verifying the message’s original content and ensuring it hasn’t been altered is part of the decryption procedure.
Authentication:
Refers to verifying a website’s or a computer user’s identity.
Data Protection:
An unauthorized third party cannot perform a data breach.
Secure Digital Signatures:
Message integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation are provided through digital signatures.
Data Security through Encryption:
refers to the techniques discussed above to ensure data security using a combination of public and private keys that represent asymmetric cryptography.
Wrap Up!
The challenges of email security and data confidentiality can be removed by implementing a S/MIME certificate all over your organization’s email systems.
In addition to having the confidence that your organization’s identity has been verified, you can do business operations with confidence knowing that your communications are encrypted, and the integrity of your attachments is secured.
FAQ’s
What is the Main Purpose of S/MIME?
Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension is a method or technology that’s frequently used by companies to enhance email security. It offers encryption, which shields email messages’ information from unauthorized access.
What are the 4 Key S MIME Services?
Authentication, message integrity, non-repudiation of origin, and message privacy are the four fundamental security services provided by S/MIME.
What is the Validity Period of the S/MIME Certificate?
The maximum validity period of the S/MIME certificate is 3 to 4 years.
What Benefits can a S/MIME Provide to your Organization?
- Organisation Reputation
- Reducing risk for businesses
- Preventing the theft of identities
- Minimizing compliance risks and related costs
What is the Difference between SMIME and SMTP?
The maximum line length for SMTP is 1000 characters in 7-bit ASCII text. Rich words, images, and music and video files are examples of the more advanced file formats that MIME can support.
Digitally Sign your Email and Documents with Trusted SMIME (Email Certificates) Starts at Just $12.99 Per Year
