What is the Difference between DNS over TLS vs DNS over HTTPS?
The key differentiation between DNS over TLS (DoT) and DNS over HTTPS (DoH)
DNS over TLS (Transport Layer Security) and DNS over HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are two protocols designed to encrypt DNS queries and responses to improve privacy and security.
This article provides the fundamental difference between DNS over TLS vs DNS over HTTPS
What is DNS?
DNS is an abbreviation for Domain Name System. Domain names are part of this system. DNS contains critical information such as text entries, email server details, domain names, domain ownership, etc. It functions similarly to a phone directory. If you know the person’s name, you may look up the phone number in the DNS phone book. Its most significant job is to provide internet services to protocols. It is a decentralized and structured naming system for services, computers, and other resources connected to the Internet or any private network. It resolves the domain name entered by the browser to the IP address of its hosted web server.
The DNS name server holds the DNS records. It defines the data definition with technical functionality. Authoritative DNS and Recursive DNS are the two types of DNS services. This is a crucial security and privacy element for both businesses and consumers. The DNS protocol is essential to the operation of the internet.
What is TLS?
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is an acronym for a security protocol that emerged from the development of Secure Socket Layers (SSL) by Netscape Communications Corporation in 1994. TLS is widely employed in securing online communication and transactions. It provides communication security to protocols that are in use. TLS is a cryptographic protocol that ensures the security of data transferred between apps over the Internet.
It is most often associated with secure online browsing, including the padlock icon that shows in web browsers when a secure session has been established. However, it can and should be used for other applications, including e-mail, file transfers, video/audioconferencing, instant messaging, voice-over-IP, and Internet services like DNS and NTP. It will protect the data and information when communicating online.
The primary goal of TLS is to offer privacy and security for website information and data.
What is DNS Over TLS? (DoT)
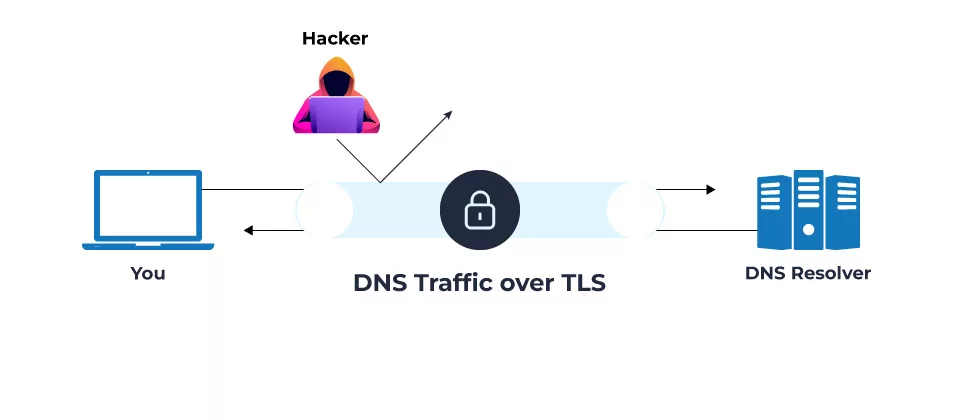
The DNS over TLS is a security protocol; it can encrypt and protect Domain Name System requests and resolve them using the TLS protocol. DNS over TLS protects the confidentiality of DNS clients and DNS servers. The abbreviation for DNS over TLS is DoT. The DoT protects and encrypts information while also resolving DNS queries. DoT blocks unwanted and unusual details, and attackers cannot hack any information or data on the website. DoT employs TLS to encrypt DNS UDP queries and responses, ensuring these messages’ integrity and confidentiality during transmission.
How Does DNS over TLS work?
DNS over TLS is a very basic and easy-to-use protocol. DNS over TLS improves connectivity between DNS clients and DNS servers. The main objective of DNS over TLS is to secure and encrypt DNS information during communication or data transfer.
- Session initiation is the preliminary step in DNS over the TLS server version. The DNS over TLS must accept the TCP connection on Port 853. All TCP connections should be secure and encrypted when doing this and using DoT. This is essential for data security and protection when utilizing DNS over TLS.
- The TLS connection will undergo the authentication process. After connecting with the DNS clients, the DNS servers will begin the TLS handshake and authentication procedure. Once a connection is established between DNS clients and DNS servers, complete encryption will be performed.
- DNS over TLS helps protect against DNS snooping and man-in-the-middle attacks, which can intercept and alter DNS queries. It also protects your privacy by preventing unauthorized parties from obtaining sensitive information like your browser history and online activity.
What is DNS Over HTTPS? (DoH)
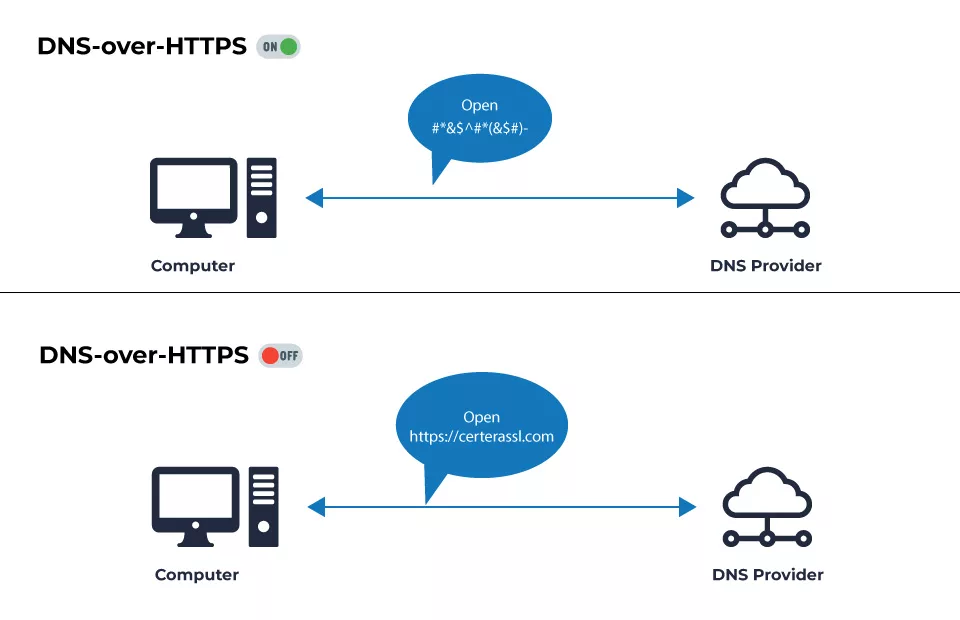
DNS over HTTPS (DoH) is a protocol that encrypts and transmits DNS queries and replies over HTTPS, the same protocol used for protected and secure web browsing.
DoH, or DNS over HTTPS, is an alternative to DoT. DNS requests and responses are encrypted using DoH; however, they are sent over the HTTP or HTTP/2 protocols rather than directly over UDP. Like DoT, DoH ensures intruders cannot forge or modify DNS traffic. It uses the HTTPS protocol to encrypt data sent between DNS clients and DoH-based DNS resolvers. Google and Mozilla started using DoH to encrypt their data and information in 2018. This is the enhancer that will boost the website’s privacy and security. No one can access your website’s information if you use DNS over HTTPS. This will increase encryption and security for both the user and the organization.
How Does DNS over HTTPS work?
- When a user enters a URL or clicks a link, their device sends a DNS query to a DNS server to determine the IP address associated with the domain name. The DNS server responds with the IP address, and the device can subsequently connect to the website.
- This request and response occur in clear text in a typical DNS resolution procedure, which implies that anyone on the network may intercept and potentially modify them. The DNS over HTTPS, on the other hand, encrypts DNS queries and responses with HTTPS, making it more difficult for outsiders to eavesdrop, manipulate, or redirect them.
- DoH requires configuring the device to utilize a DoH-compatible DNS server. When a user inputs a URL, the device encrypts the DNS query and sends it to the selected DoH-compatible DNS server over an HTTPS connection. The server encrypts the response and sends it back to the device. DoH can increase privacy and security while circumventing certain forms of restriction and filtering.
How DNS over TLS vs DNS over HTTPS are Different?
TLS and HTTPS both encrypt DNS requests. However, there are a few significant differences between DNS over TLS vs HTTPS.
| DNS over TLS (DoT) | DNS over HTTPS (DoH) |
| DNS over TLS uses TCP port 853 | DoH employs TCP port 443, which is also used for HTTPS communication. |
| DNS over TLS uses TCP as the standard connection protocol and TLS authentication and encryption layers. | DNS over HTTPS uses HTTP/2 and HTTPS as the standard connection protocol. |
| The IETF defines DNS over TLS as RFC 8484. | The IETF defines DNS over HTTPS as RFC 8310 and RFC 7858. |
| DoT provides great privacy and security since it uses TLS, which is a proven and widely deployed security protocol. | DoH is frequently easier to implement and is more widely supported by web browsers, making it easier to scale. In addition, DoH traffic is less likely to be intercepted by firewalls and other network filters. |
Which is better: DNS over TLS vs DNS over HTTPS?
This is debatable. Your requirements and circumstances will determine which protocol is most effective (DNS over TLS, DNS over HTTP) for you. While both protocols aim to improve the privacy and security of DNS queries, their approaches to encryption and the transport layer protocol are different. Users might prefer DoH since it allows them to evade some network filters, although DoT is typically seen as more secure due to its use of the well-established TLS protocol.
DoT is perhaps better in terms of network security. It enables network managers to monitor and prevent DNS requests, which is essential to detecting and preventing unwanted activity. Meanwhile, DoH requests are concealed in regular HTTPS traffic, making it difficult to prevent them without also blocking all other HTTPS traffic.
However, DoH is perhaps preferable in terms of privacy. DNS requests are hidden inside the wider flow of HTTPS communication when using DoH. This reduces network managers’ visibility while increasing user privacy.
FAQ’s
What is DNS over HTTPS/TLS?
DNS over TLS, or DoT, is a security and privacy standard for encrypting DNS requests. To encrypt and authenticate connections, DoT employs the same security standard, TLS, as HTTPS websites.
What is the difference between DNS, HTTPS, and TLS?
The IETF defines DNS over HTTPS as RFC 8484, whereas DNS over TLS is RFC 7858 and RFC 8310, respectively. In DNS over TLS, the base connection protocol utilized is TCP, which then incorporates layers of encryption and authentication through TLS. HTTPS and HTTP/2 are used in the DNS over the HTTPS connection.
Is DNS over HTTPS slower?
Often privacy and security are frequently paid for by a decrease in connection speeds. After all, there is more data and web traffic to encrypt and decode. Thus, secure communication will take a little longer than unsecured communication.
What are the disadvantages of DNS over HTTPS?
Potential Performance Issues: One of the possible downsides of using DNS over HTTPS is that it might degrade performance. Because the data is encrypted, communication between the DNS client and the DNS resolver takes longer. This can result in slower page loads and other performance issues.
Does DNS over TLS increase latency?
Connection-oriented, secure DNS protocols will incur additional delay; however, these costs may (and are) often amortized by caching the DoH resolver’s DNS name and multiplexing several DNS requests over a single TLS session to a DoH resolver.
