How Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Works to Keep Your Data Secure?
Securing Digital Communication: The Vital Role of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
With increasing cyber threats, robust data encryption has become crucial to any organization, regardless of dimension or sector. Encryption is the process of converting plaintext into ciphertext, rendering it unreadable to unauthorized users. It plays a crucial role in data security, as it safeguards sensitive information like credit card numbers, passwords, and confidential data stored online, ensuring their protection from unauthorized access.
Encryption can be achieved in various approaches, but Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is typically identified as one of the most effective data security techniques. It guarantees that data is adequately encrypted during transit and that only authorized users can access it. It is one of the most important ways to protect communication and reduce data breaches. Additionally, it regulates the issuing of digital certificates to secure end-to-end communications, protect sensitive data, and give unique digital identities to people, devices, and applications.
Let’s have a look at “how public key infrastructure works” and “how it provides a way for secure encryption in organizations.”
What is Public Key Infrastructure?
The term public key infrastructure refers to the digital program or process used to generate and maintain public keys for encryption, which is an effective way of protecting data transfers over the internet. All the latest web browsers have integrated it, and it actively contributes to securing public internet traffic. Organizations may use it to protect internal communications and ensure that connected devices can communicate securely.
The most crucial concept associated with PKI is the cryptographic keys that are part of the encryption process and help authenticate different individuals or devices seeking to connect with the network.
What is the need for Public Key Infrastructure?
PKI is significant because it provides a safe and dependable way to certify the identity of communication parties and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data exchanged through networks. It achieves this using digital certificates and public and private key encryption.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) ensures secure online transactions, including e-commerce, online banking, and government services. It is also important for secure communication among personnel inside an organization, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data, and protecting against harmful attacks.
PKI plays a crucial role in today’s digital era as increasing private information is shared online. Organizations may use this secure method to assure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data and transactions, ultimately building trust and protecting their confidential information.
You may be wondering what Public Key Infrastructure security looks like in your everyday life; this proficient security mechanism is used in a variety of ways, but it is typically used for:
- Email Security
- Web Communication Security
- Signing Apps Digitally Signed Apps and Software
- Authentication Using a Smart Card
- File Encryption and Decryption
- Restricted access to VPNs and Business Intranets
- Secure interaction among mutually trusted devices such as IoT (Internet of Things) devices
How does PKI Work?
In simple terms, public key infrastructure is a framework for protecting communications between multiple computer systems (based on encryption key pairs and digital certificates). It’s also an approach that helps your company comply with regulatory data security and privacy regulations, avoiding penalties, fines, and harm to its reputation.
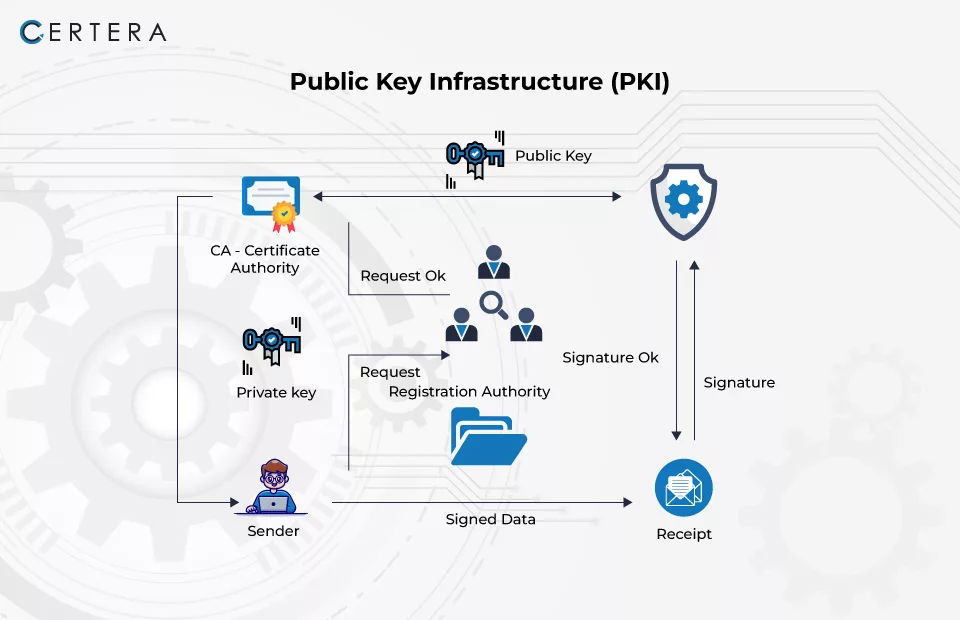
PKI employs cryptographic public keys connected to a digital certificate to authenticate the device or user transmitting the digital connection. An authorized organization, referred to as a certificate authority (CA), issues digital certificates, which function as a digital passport, verifying the sender’s identity. Certera, Comodo, and Sectigo are some of the well-known Certificate Authorities.
The following are the Primary Components of Public Key Infrastructure(PKI):
- Certificate Authority
- Registration Authority
- Certificate Database
- Central Directory
- Certificate Policy
- Certificate Management System
The Certificate Authority (CA) is a trustworthy organization that issues maintains, and signs digital certificates. The certificate authority (CA) signs the digital certificate using its private key and publishes the public key, which can be obtained upon request.
The Registration Authority (RA): It authenticates the individual or device looking for the digital certificate, which might be a third party or the CA serving as the RA.
Certificate Database: It maintains the digital certificate and its metadata, including its validity period.
Central Directory: It is the safe and protected place where the cryptographic keys are indexed and kept.
Certificate Policy: The PKI processes are outlined in this policy. Outsiders could use it to determine the trustworthiness of the PKI.
Certificate Management System: It is the system that manages the delivery and access to certificates.
Now let’s figure out how PKI works
- PKI uses Asymmetric Encryption techniques to ensure that communications remain private and authenticate the device or individual delivering the data to be transferred.
- The method of Asymmetric Encryption utilizes a public and private key pair. A cryptographic key is a long string of bits that is used to encrypt data.
- The public key is available to everyone who requires it and is issued by a trusted certificate authority; this public key verifies and authenticates the sender of the encrypted communication.
- The private, or secret, key is the second component of a cryptographic key pair in public key infrastructure; this key is kept secret by the recipient of the encrypted communication and is used to decrypt the message being transmitted.
- Complex mathematical algorithms are used to encrypt and decode public/private key pairings. The public key authenticates the sender of the digital communication, while the private key assures that only the receiver can access and read it.
Different Stages Involved in PKI Work Process
- Key Pair Generation: The user creates two keys: a private key and a public key.
- Certificate Request: The certificate request is sent to the Certificate Authority (CA). The user’s public key and identity details are included in the request.
- Certificate Issuance: The CA checks the information in the request and validates the user’s identity. After successful verification, the CA provides the user with a digital certificate, including the user’s public key, identity information, and the CA’s digital signature.
- Public Key Distribution: The user’s digital certificate is then given to parties who require it to connect securely with the user via various channels.
- Data Encryption and Digital Signature: When a user wants to send a secure communication to another entity, the user encrypts the message using the recipient’s public key, ensuring that only the recipient can decrypt the message using their corresponding private key. The user signs the message with their private key to ensure identity authentication and message integrity.
- Verification: After receiving the message, the receiver validates the digital signature using the sender’s public key to confirm its validity and integrity. The communication is then decrypted by the receiver using their private key.
- Revocation: If a client exhibits suspicious behavior or loses trust in them, the CA can revoke the digital certificate.
Public Key Infrastructure enables reliable and secure digital communication and data communication.
PKI Use in the Modern Digital Age:
Public Key Infrastructure: It is essential for enabling secure online communication and transactions in today’s digital era.
Here are some examples of Public Key Infrastructure applications in today’s world:
Secure authentication: PKI authenticates the identity of individuals or devices and ensures communication security. For instance, it verifies your identity and encrypts communication between you and the server when accessing your bank account or logging into an organization’s network.
Basic security method: Public Key Infrastructure has existed for decades and is already present in many company IT infrastructures. Several types of software, from email clients and servers to web servers and operating systems, currently support PKI certificates.
Secure mail communication: It encrypts and signs emails, ensuring data confidentiality and verifying the sender’s identity.
Digital signatures: It generates and validates digital signatures, ensuring the validity and integrity of documents and information. It is especially significant in areas where document authenticity is essential such as healthcare, legal, and government.
Online transactions: It secures online transactions, including e-commerce and online banking, by encrypting communication between the user and the server and validating the identities of both parties.
Challenges that PKI overcome:
PKI owes its popularity to the various problems it solves. Some use cases of PKI are:
- Protect browsers and networks with TLS or SSL Certificate.
- Keeping Access Rights on Intranets and VPNs.
- Verifies the identity of the server connected with the public key.
- Wireless Internet Access Without Passwords
- Digitally Signed Software
- Encryption of data
- Scalability
- Compliance
- It provides methods for revoking compromised or expired digital certificates, preventing them from being used to authenticate activities.
Aside from this, one of the most prominent Public Key Infrastructure use cases focuses on IoT (Internet of Things).
Public Key Infrastructure enables reliable connections between networked devices, services offered by the cloud, smart infrastructures, and “things.” This is the authentication component that IoT requires for security. PKI excels as a proven solution in several areas of security. For instance, manufacturers of automobiles and medical devices.
Conclusion
Encryption is critical for securing and protecting data in today’s digital environment. PKI is a robust security technology that employs digital certificates to authenticate the identity of individuals and organizations, ensuring that only authorized users have access to confidential information; this article provides a detailed picture of “how PKI authentication works” along with its applications and functions.
By following these key steps, organizations can implement a robust PKI system that secures their digital assets and protects against cyber-attacks.
FAQs
1. How does PKI work with encryption?
PKI uses asymmetric encryption techniques to ensure that communications remain private and to authenticate the device or individual sending the data to be transferred. Asymmetric encryption employs a public and private key pair. A cryptographic key is a long string of bits that is used to encrypt data.
2. What are the PKI encryptions and algorithms available to secure the information?
Public Key Infrastructure uses symmetric and asymmetric encryption to secure all its assets. Asymmetric encryption, also known as Public Key Cryptography, uses two distinct keys for encryption and decoding. One is referred to as a public key, while the other is referred to as a private key.
3. Which PKI key is used to encrypt?
Typically, we encrypt the data using the receiver’s public key, and the recipient decrypts it using their private key. However, no method exists to validate the message’s source using the digital signature scheme.
4. What are the five main components of PKI?
Types and Components of Public Key Infrastructure
- Certificate Automation
- Trusted Identities
- The Signing of Code.
- Digital signatures
- Qualified trust
5. Where is PKI used?
PKI is used in a variety of applications. It is utilized in smart card logins, XML document encryption, secure email communications, and client system authentication. PKI is utilized in all circumstances where data security is critical.
