How to Fix the SSL/TLS Handshake Failed Error?

An SSL Handshake failure error occurs when a secure connection between a server and a client fails to establish. If you are familiar with the SSL Handshake process or using an SSL certificate, you must understand why such an issue occurred on your system. In this article, we will not only outline an SSL handshake but also discuss why this error comes up and how to fix the SSL handshake failed error.
What Is SSL Handshake?
An SSL handshake establishes a secure connection between the web server and the client (such as a web browser). The initial stage in the SSL/TLS connection process enables two parties to communicate securely over the Internet.
During an SSL handshake, the client & server establish an encryption connection and use digital certificates to verify each other’s identities. There are multiple phases in the SSL handshake process, including:
- The client’s system initiates the SSL handshake process by sending a request to connect to the server.
- The server sends its SSL certificate to the client, which includes its public key.
- The client checks the SSL certificates and gets the public key.
- The client generates a random encryption key and encrypts it using the server’s public key.
- The encrypted key is sent to the server by the client.
- The server decrypts the encrypted key using its (server’s) private key.
- Both the server and the client use the encryption key to establish a secure connection.
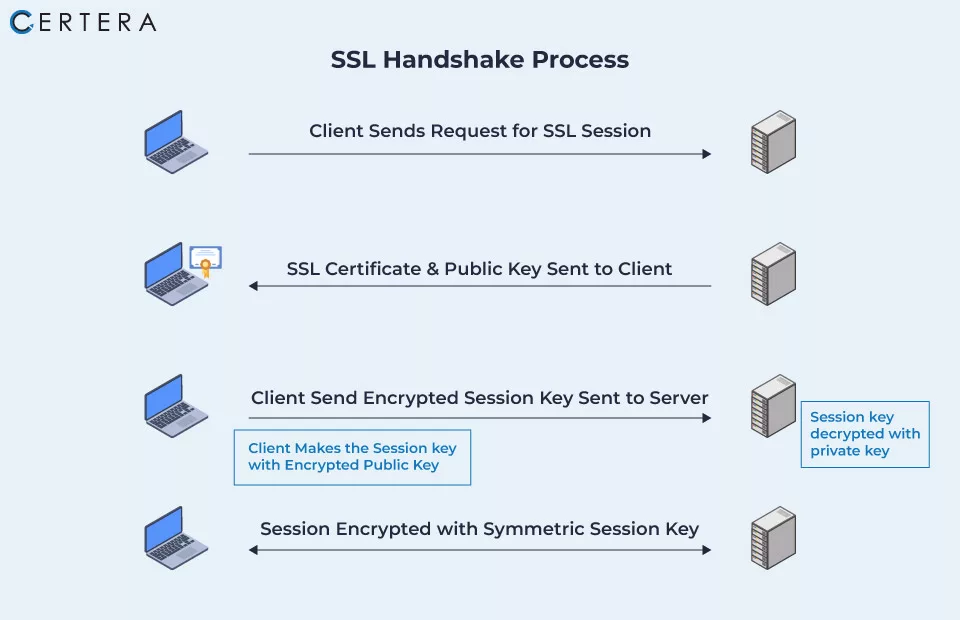
Once the SSL handshake is complete, the browser and server can securely transmit the data; the process is secure against eavesdropping, manipulation of data, and other security concerns and is essential in ensuring a secure connection.
Learn how SSL Certificate Works.
Why does ‘SSL handshake failed’ error occurs?
The SSL Handshake error, also known as error 525, occurs when two endpoints (server and client) fail to establish a secure connection. There are many reasons the handshake gets failed from the client side as well as the server side. Les takes a look at the top reasons for this error.
An “SSL Handshake Failed” issue can occur for a variety of reasons, including:
- Incorrect Date and Time settings
- Invalid SSL/TLS Certificate
- Incorrect Cipher Suite Selection
- Interference with SSL handshake by firewalls or proxies
- Network connectivity
- Server Configuration Issues
- Incompatible protocol versions
Incorrect Date and Time Settings
SSL/TLS depends extensively on accurate system time settings. If the client or server device’s date and time are wrong, your system will encounter with “SSL Handshake Error.”
Invalid SSL/TLS Certificate
If the SSL/TLS certificate on the server or client side is expired, untrusted by the client, or incorrect, the connection cannot establish, resulting in SSL Handshake Error.
Incorrect Cipher Suite Selection
This error might occur if the server and client use different cipher suites for SSL/TLS connection.
Interference with SSL handshake by Firewalls or Proxies
Firewalls or proxies may block SSL handshake packets or attempt to “man-in-the-middle” the communication by substituting an incorrect SSL/TLS certificate.
Network connectivity
An SSL handshake failure might occur if network communication between the client and server is disrupted.
Server Configuration Issues
If a configuration issue on the web server occurs, such as deactivating SSL or TLS, the SSL handshake may fail.
Incompatible Protocol Versions
An SSL handshake could fail if the client and server use incompatible SSL/TLS protocol versions.
Fix the SSL Handshake Failed Error
You can fix the Handshake Failed Error in many ways. Here are a few examples.
- Correct the System Date and Time
- Update Your Web Browser
- Check that your browser supports the most recent TLS protocol
- Check whether the certificate is valid or not
- Deactivate any new plugins or extensions that have been installed
- Check Your Server Configuration
- Use compatible ciphers
1. Correct the System Date and Time
An incorrect date or time configuration is one of the most common reasons for SSL/TLS handshake problems. Since the system time is used to determine whether the certificate is valid or expired, a time or date difference between your device and the server might cause the certificates to seem expired.
Set the time and date to automatic, and then return to the site to verify whether the TLS handshake problem has been resolved.
A Windows user may take the following steps to reset the date and time:
- Click on the ‘Windows’ button.
- Enter ‘Date and Time Settings’
- Toggle the set time automatically’ button to set the time automatically.
- If you are using a VPN or need to manually set the time for any other reason, use the ‘Set the date and time manually‘ option.
The same thing may be done on a Mac by going to ‘Menu’ and then ‘System Preferences.’ All other operating systems provide similar settings.
2: Update Your Web Browser
You must always keep your operating system, browser & software programs current. Doing so can avoid such critical problems, including the ‘SSL handshake failed’ error.
- In Chrome, Check the top right corner > if there is an update, you will see the “Update” button > Click on it to update your Chrome.
- In Firefox, Click on the top right corner (Three Horizontal Lines) > Click on Help > About Firefox > Click on Update Firefox.
3. Check that your Browser supports the most recent TLS Protocol
Verify that your web browser holds the most recent TLS protocol. Due to browser issues with the TLS version, you may get the “SSL handshake failed” error in some circumstances. The most common problem is that your browser does not support the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol used by your certificate. SSL and TLS are both authentication methods, and your certificate may utilize either. Both protocols are supported by modern browsers, while some older ones may not. Using a different browser is the simplest approach to test whether your browser is causing the problem. If the “SSL handshake failed” message does not occur in other browsers, the issue might be with the original one.
To resolve this issue on Windows, go to the Start menu and search for Internet Options. Go to the Advanced tab after selecting the option that displays. Scroll down the list of choices until you reach the options for SSL and TLS settings:
- Configuring the TLS protocols supported by your connection If you see those options, you can uncheck the SSL 3.0 and SSL 2.0 boxes.
- You simply need to check the TLS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 boxes.
- Then save the changes to your internet settings and try to visit the page again. TLS 1.2 should be enabled by default if you’re using macOS or iOS.
4: Check whether the Certificate is Valid or Not
If the SSL certificate is no longer valid or expired, you will immediately get an “SSL Handshake Error.” You will get the same error even if you do not buy SSL from a legit certificate authority such as Comodo, Sectigo, or Certera.
SSL establishes a secure link between the browser and the server. SSL ensures the privacy and security of any data transmitted between these two. As passionate internet users, we can navigate safe online environments thanks to SSL.
Security certificates do expire since they have a validity period. These dates are essential for maintaining SSL security. The validity period regulates and validates server legitimacy, letting your web browser identify the server. Users must know what happens when SSL Certificate expires.
5: Deactivate any New Plugins or Extensions Installed
Unidentified people generate most browser plugins and extensions and may contain malicious software. If you recently installed one of these and are experiencing SSL handshake issues, consider removing it as well as cleaning your cache and cookies. Reconnect to the same website to test whether you can establish a secure connection.
Chrome users can remove the extension by following the steps outlined below:
- In the upper-right corner, click the three vertical dots.
- Choose ‘Settings.’
- Select ‘Extensions.’
- Select the newly installed extension and click Remove.
Firefox Users can remove the Addon using the following steps
- Click on the top right corner (three horizontal lines)
- Select Add-ons and Themes or press Ctrl + Shift + A
- Check for the recently added “Add-ons” and remove them.
6: Check Your Server Configuration [for SNI Support]
One of the primary reasons for TLS issues is incorrect server name indication (SNI) settings. The SNI enables the server to securely host several TLS certificates/protocols for a single IP address.
Each website on a server has its certificate. So, if the server isn’t SNI-enabled, there’s a good chance the TLS handshake will fail since the server won’t recognize the current certificate.
You can use any “SSL Checker Tool” to determine whether the site uses SNI. You’ll need to enter your website’s domain name, then click Submit and wait for the results.
7: Use Compatible Ciphers
Incompatible cipher suites can potentially cause the SSL/TLS handshake to fail. To resolve this, the site administrator should verify that the server is configured with cipher suites that the web browser recognizes. This may be accomplished by either changing the cipher suite list or activating and disabling individual ciphers in the server settings.
Conclusion
Since the SSL Handshake plays an essential part in ensuring the security of data in transit, users must understand “what exactly the SSL Handshake failed error means” and “how to resolve it”. We’ve gone through some of the most efficient fixes for the SSL handshake problem, which might be caused by browser or system settings.
This typical problem may be resolved by performing the appropriate measures. By following the procedures outlined above, you can ensure that your website users may access your site securely and without trouble.
FAQ’s
What are the common reasons for SSL handshake failure?
The most common reasons for SSL handshake failure are certificate errors, incompatible protocols or cipher suites, incorrect server name indication (SNI), Firewall or NAT issues, time synchronization errors, new plugins or extensions that have been installed, and Malware or virus infections, etc.
How do you resolve handshake failure?
- Update the date and time on your system.
- Check the validity of your SSL certificate.
- Configure Your Browser to Support the Most Recent SSL/TLS Protocols.
- Check that your server is set up correctly to support SNI.
- Check that the Cipher Suites match.
Can a firewall block an SSL handshake?
Yes, a firewall may block an SSL handshake. Firewalls can analyze SSL traffic and block connections to certain locations based on the network administrator’s security policies or rules. These rules can be based on various traits, such as source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, domain names, and SSL certificates. If the SSL traffic does not comply with these requirements, the firewall might block it, preventing the SSL handshake from occurring.
What is the high response time for an SSL handshake?
A high response time for an SSL handshake can vary based on factors such as server load, network latency, and client configuration, but anything greater than one second is considered high.
Usually, for persistent sessions, partial handshakes, and complete handshakes, the average CPU per request is 0.339 ms, 0.505 ms, and 0.652 ms, respectively.
What is dropped due to failed client SSL handshake?
Hardcoded certificates, custom trust stores, or other temporary challenges might cause client-side SSL handshake failures. If you check the SSL failed handshake reason and count, you will find the cause for the failure (based on TLS RFC alert codes)
How many packets are in the SSL handshake?
The SSL handshake processes normally consist of two packets: the Client Hello and the Server Hello. However, depending on the protocol and encryption parameters used, more packets may be transmitted during the handshake phase.
