How Does SSL Certificate/HTTPS Work?

As the internet evolves, the techniques for improved website security increase, and so does malicious cyber attackers’ creativity. Moreover, internet security becomes essential as organizations provide more online services and transactions. To keep client information private and secure, businesses and organizations must add SSL certificates to their websites to enable secure online transactions. SSL certificates establish the groundwork for a secure connection by providing a secure connection. To assure visitors that their connection is secure, browsers display unique indications known as EV indicators, ranging from organization name in Certificate Information to Site Seal.
This article lets us understand “What is an SSL certificate,” “How does SSL work/How HTTPS works,” and “What are the various types and benefits of SSL.”
Let’s Dive in
What is an SSL Certificate?
SSL Certificates, also known as Secure Sockets Layer Certificates, are digital security certificates that enable secure communication between a website and its visitors. A trusted and legitimate third-party organization, a Certificate Authority (CA), issues the SSL certificate. Including Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) in the website URL denotes using an SSL Certificate.
SSL Certificates contain information like the certificate owner, expiration dates, serial numbers, etc., allowing browsers to verify the website’s identity and establish a secure connection.
How Does SSL Certificate Work?
In this section, let’s figure out how an SSL works,
When a browser requires access to an SSL-secured website, the browser and web server establish an SSL connection using a procedure known as an “SSL Handshake” (as shown in the diagram below). It is essential to note that the SSL Handshake is completely transparent to the user and takes place instantaneously.
The Public Key Infrastructure, the mixture of public, private, and session keys, is used to establish an SSL connection. Any message encrypted with the public key must be decrypted with the private key and vice versa. Since encrypting and decrypting using private and public keys requires significant computing power, they are only utilized to generate a symmetric session key during the SSL Handshake. After establishing a secure connection, the session key encrypts all transferred data.
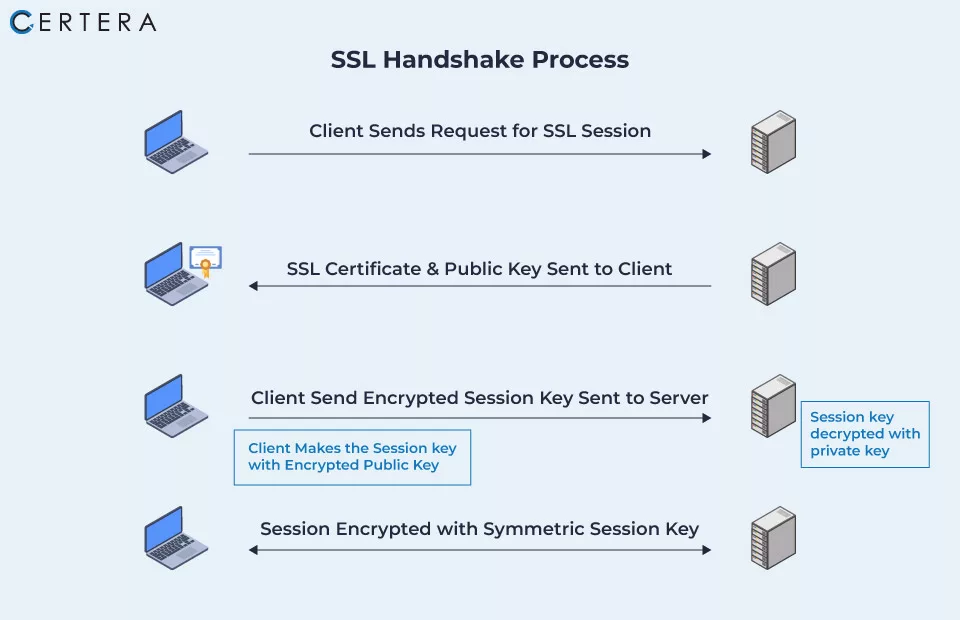
- The browser attempts to connect to an SSL-secured web server (website). The browser asks the server to identify itself.
- The server sends a copy of its SSL, which includes the public key.
- The browser verifies the certificate root to a list of legitimate CAs and ensures that the certificate has not expired or been suspended and its common name remains active for the website to which it is connected. If the browser trusts the certificate, it produces, encrypts, and sends a symmetric session key using the server’s public key.
- To start the encrypted session, the server decrypts the symmetric session key using its private key and sends back an acknowledgment encrypted with the session key.
- The session key is now used to encrypt transmitted data by the server and browser.
What is the need for an SSL certificate?
- Secure Data Transmission
- Authenticity
- Increased Trust
- Compliance
- Protection from Top 5 Risks
Secure Data Transmission
SSL certificates offer a secure connection between the server and the client, ensuring that data is encrypted and secure from hackers and unauthorized access.
Authenticity
It protects against phishing attempts by affirming the authenticity of a website, making it impossible for attackers to establish fraudulent websites and fool users.
Increased Trust
Sites with SSL (HTTPS) display a padlock icon and the HTTPS protocol in their web address, giving users confidence that their data is secured and that the site is trustworthy.
Compliance
Certain businesses, such as healthcare and finance, have regulatory restrictions requiring the usage of SSL certificates to secure sensitive data.
Protection from the top 5 Risks
Using an SSL certificate will let you free from MITM attacks, confidential data leakage, Phishing Attacks, damage to reputation, and distrust by web browsers. If your website does not have an SSL certificate loaded, all communications from the web server to the client are not encrypted. Intruders can easily compromise these forms of unprotected and unsecured communications.
SSL certificates provide trust, security, and compliance, making them an essential tool for businesses and organizations that value their online presence and reputation.
Types of SSL/TLS Certificates
Domain Validated (DV) Certificate
It validates the website’s domain name. It is the simplest & quickest to get, requiring minimal personal identifying verification. A DV-secured website displays a locked padlock in the URL bar, HTTPS, and Site Seal.
Organization Validated (OV) Certificate
This SSL/TLS certificate type confirms the organization’s domain name and legal presence. It has greater encryption levels and requires more comprehensive authentication to obtain. The CA validates that the organization is officially and legally allowed to do business.
Extended Validation (EV) Certificate
Most internet users opt for EV SSL certificates because they offer the most thorough verification testing, which includes domain verification and crosschecks that connect the entity to a specific physical address. EV certificates give website users the greatest level of authenticity and confidence. It verifies the domain name, the organization’s legal existence, and the organization’s geographical location.
Other SSL Types:
Please remember that the three types of SSL certificates listed above are not the only ones available. Other types of certificates include:
Wildcard SSL
Wildcard SSL is a special SSL that can safeguard unlimited subdomains under a single domain. It enables the configuration of encryption for an entire domain and its subdomains. Wildcard SSL comes with domain validation and organization validation.
Learn more about What is Wildcard SSL Certificate and how it protects sub-domains.
Multi-domain SSL
It allows you to secure multiple domains (up to 250) with one SSL certificate. All the domains secured by a multi-domain SSL share the same CSR details, issuer details, and validity period, which binds them together under one SSL.
Use SSL Certificates to Secure your Website.
SSL Certificates/HTTPS function encrypts data transmitted between a website and a user with a public-private keypair, providing a secure communication channel. The SSL also validates the website’s validity and offers various advantages, such as improved SEO ranking and cyber-attack protection.
You may always get an SSL to protect your website connection and customer data, leading to greater revenue and a higher Google ranking.
Approximately 85% of website owners select the incorrect SSL for their online business. Be not one of them.
- Select the appropriate SSL for your website by visiting our website, certera.com.
- Certera offers SSL certificates from three vendors: Certera, Comodo, and Sectigo.
- Pick up the Most relevant SSL to secure your website.
- Generate CSR and Private Key
- Issue the Certificate by verifying Domain Name and Organization Details.
- Install the SSL Certificate on your Server
- Finally, your website is secured with SSL.
FAQ’s
1. What happens if you do not have an SSL Certificate?
Without an SSL, your website will show “Not Secure” in the address bar, informing users that your website cannot be trusted, possibly resulting in decreased visitor numbers.
Not implementing an SSL on your website exposes your business and clients to threats such as Data leaks, Man-In-The-Middle, Phishing, etc.
Learn what happens if your SSL Certificate expires.
2. Is it free to get an SSL Certificate?
To understand the key difference between free and purchased SSL certificates, you must first become familiar with the phrase “certificate authority.” Non-profit certificate authority issues free SSL: Let’s Encrypt, a renowned non-profit CA, offers free SSL/TLS certificates. They aim to encrypt the whole internet so that HTTPS becomes the standard. Still, they have many drawbacks regarding security, encryption, and privacy. There are significant benefits of using paid SSL certificates over free SSL in terms of SSL Certificate Lifespan, SSL Options, etc.
3. How to get an SSL Certificate?
The steps for getting an SSL are as follows:
- Make sure you have the right website information.
- Choose the type of SSL you require.
- Selecting a Certificate Authority (CA)
- Create a Certificate Signing Requirement (CSR).
- Submit the Certificate Signing Request (CSR) to a Certificate Authority (CA).
- Awaiting validation from the CA
- Install your SSL certificate.
4. What is the Cost of an SSL Certificate?
The cost of an SSL varies from the number of domains and sub-domains they cover and the type of validation process required to get them.
- SSL certificates with domain validation cost less than SSL with Organization or Extended Validation.
- If a user purchases SSL Certificate for multiple years, they will get more discount compared to 1 or 2 years.
- Purchasing SSL certificates directly from Certificate Authority may cost you high, but if you purchase SSL from trusted Providers like Certera, you will get a huge discount.
Top SSL Certificate with Lowest Price
| SSL Certificate | Price per Year |
|---|---|
| Certera SSL Certificate | $3.99 |
| Certera Wildcard SSL Certificate | $39.99 |
| Certera Multi-Domain SSL Certificate | $9.99 |
| Comodo PositiveSSL Certificate | $7.49 |
| Comodo Positive Wildcard SSL | $45.99 |
| Comodo PositiveSSL EV Certificate | $60.99 |
| Certera Multi-Domain Wildcard SSL | $39.99 |
5. Do SSL Certificates Expire?
SSL Certificates have a specified expiry date, unlike other services that renew automatically until explicitly canceled. Allowing an SSL Certificate to expire can have serious consequences for the website owner and the end user. When they expire, web browsers will warn their users about your website. The reason SSL certificates expire is to keep your encryption up to date. By requiring you to renew your SSL certificate, you’ll always have the latest TLS versions and ciphers.
6. What is HSTS?
HSTS, or HTTP Strict Transport Security, is a security feature that helps prevent websites from being accessed over the insecure HTTP protocol. Once a web browser enables HSTS for a domain, it will automatically convert all HTTP requests to HTTPS for that domain.
Read our blog to disable HSTS in Chrome and Firefox.
7. What is SSL Offloading, and What are its Benefits?
SSL offloading is a technique where an intermediary server performs SSL decryption and encryption on behalf of the underlying application server. This allows the application server to handle only unencrypted HTTP traffic.
Benefits of SSL Offloading
- Reduced CPU Load
- Simplified Updates
- Centralized Certificate Management
