Know What is SSL Offloading and How it Works

SSL Offloading: A Breakthrough in Secure Data Transmission
In today’s world of technology, ensuring that your website is secured against cyber-attacks is essential. SSL (Secure Socket Layer) encryption is one of the most effective techniques for doing this. SSL protects sensitive data by encrypting the traffic between the user’s browser and the website’s server.
However, SSL can frequently add overhead, slowing down website loading times. SSL offloading comes into action here.
What Is SSL Offloading?
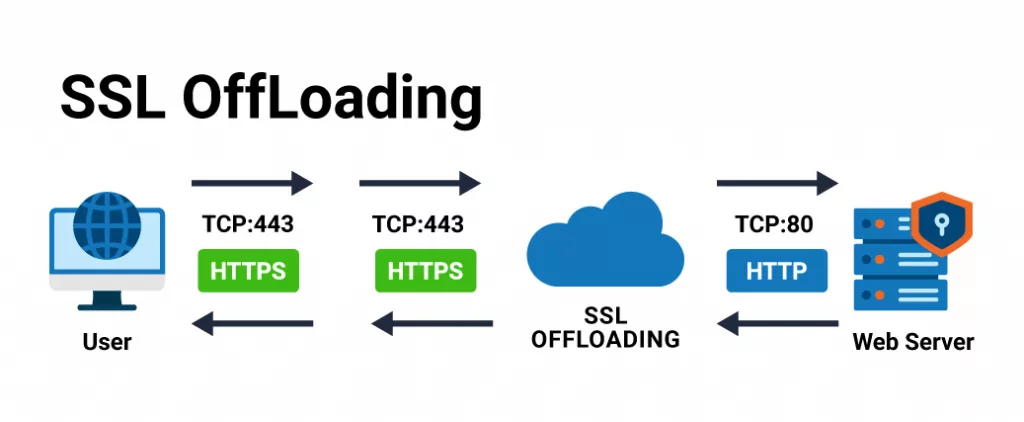
When data is transmitted via SSL/TLS Encryption, the web server encrypts and/or decrypts your online traffic; this process places a significant burden on the web server, which has an impact on its performance sometimes.
SSL offloading is used to reduce the additional load of encrypting traffic on the server; it removes SSL encryption from incoming data before it reaches the web server. SSL offloading is a method of managing the SSL process on a separate Network-Device (known as a Load Balancer) so that it has no impact on the web server’s performance, resulting in faster loading times for the users. This is majorly essential for websites that receive an excessive amount of traffic or contain resource-intensive apps.
How SSL Offloading Work?
SSL traffic is prevalent since every internet browser is compatible with the SSL/TLS protocol. The SSL offloading process is assigned to a separate device (it may be a load balancer or reverse proxy) dedicated to SSL acceleration or SSL termination. SSL certificate works by encrypting data using cryptographic keys. Earlier RSA keys with increasing key lengths (e.g., 1024 bits and 2048 bits) were one of the most often used cryptographic keys. However, shorter key length ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) keys are replacing RSA keys as the method for encrypting communications.
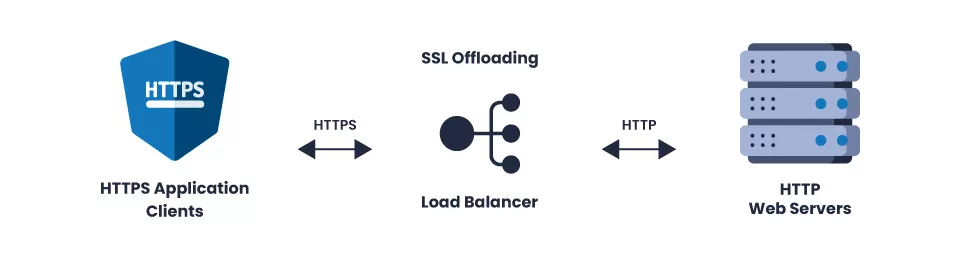
Mainly, SSL offloading is handled by a load balancer.
The load balancer is placed between the browser and the webserver to handle the task instead of the server. To execute this process, the load balancer utilizes the same SSL certificate that was previously provided to the server. A load balancer can do this task in two ways.
- SSL Termination
- SSL bridging
Let’s discuss the types of SSL offloading.
Types of SSL Offloading:
SSL Termination
In this method, SSL traffic is encrypted at the load balancer, and the load balancer sends the decrypted traffic to the web server; this offloading is widely utilized since it minimizes the server’s computing cost, consequently increasing server speed.
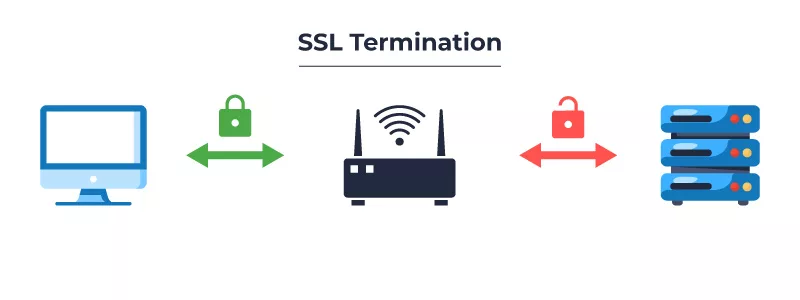
Advantages of SSL Termination:
- The server does not have to encrypt and decrypt all incoming and outgoing data. It minimizes workload and reduces processing overhead.
- It helps organizations in increasing the speed of their servers.
- SSL termination is a highly effective process for websites that do not handle critical information from users. Blogs, informative websites, and media-sharing websites (such as YouTube, Pexels, and so on) are examples.
Disadvantages of SSL Termination:
- The load balancer and server traffic is unencrypted, making it vulnerable to session hijacking, data theft, and man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks.
- The server must share the private key and the load balancer tool. It’s risky to practice.
- In certain circumstances, the SSL certificate’s purpose fails because the encryption is lost during the process.
- When your data is exposed to a third-party load balancer platform, an aspect of secrecy and privacy may be lost.
SSL Bridging
In SSL Bridging, the load balancer decrypts SSL communication & transmits it encrypted to the web server. The web server then processes the request and sends encrypted communication to the load balancer. The response is then decrypted and sent back to the client via the load balancer; this approach is less prevalent, but it provides a more secure option because communication between the load balancer and the web server is still encrypted.
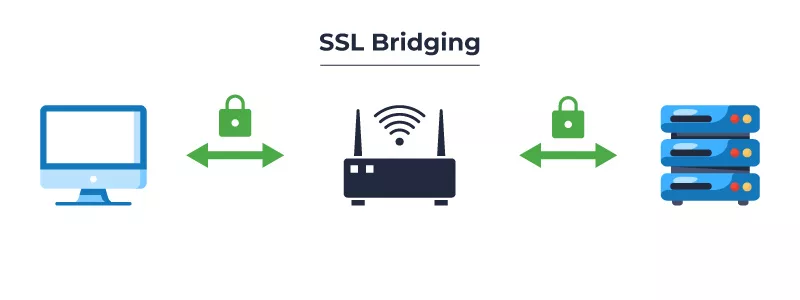
Advantages of SSL Bridging:
- SSL bridging improves security by decrypting and analyzing all encrypted data passing over the network. This helps in the detection and prevention of fraudulent activities and cyber threats.
- Better Monitoring and Control: SSL bridging gives total insight into encrypted traffic, allowing network administrators to monitor and control data flow.
- SSL bridging simplifies SSL certificate deployment and eliminates the requirement for end users to install multiple certificates.
Disadvantages of SSL Bridging:
- SSL bridging might damage performance since the decryption and inspection processes need additional CPU resources.
- For all incoming data, SSL bridging will rely on the load balancer’s AI (to examine and modify the data). If the load balancer’s AI has a false positive (considering legitimate traffic to be illegitimate by mistake) and rejects it, in resulting will also miss essential (and secure) traffic.
- It increases the complexity of the network architecture and takes more technical expertise to manage.
Benefits of SSL Offloading
Consider the amount of processing required to encrypt data. Encryption is a computationally intensive process. It means that any machine that deals with encryption may become clogged. Have you ever noticed how your PC or cell phone browser slows down while you’re doing some job online? This is because SSL increases the load.
Let’s look at some of the potential benefits of SSL offloading:
- Increased Speed
- Cost Savings
- Improved Security
- Security from Attacks
- Simplified Management
- Increased Scalability
Increased speed: SSL offloading improves web application speed by decreasing the server’s processing burden. SSL encryption necessitates a large amount of computing power, and outsourcing SSL processing to dedicated hardware or software allows for freeing up server resources for other work.
Cost Savings: By reducing the requirement for SSL-enabled hardware or software on each server, companies may save costs on licensing and hardware expenditures.
Improved Security: This can improve security by directing SSL traffic through a single or a few connections of entry. This makes monitoring and ensuring the security of SSL communications simple.
Simplified management: SSL Offloading may ease management by integrating SSL configurations on a single device or collection of devices. This simplifies the management of SSL certificates, updates, and other associated activities.
Increased Scalability: SSL Offloading makes it easier for organizations to expand their applications by minimizing the processing load on individual servers. This enables greater traffic and growth without compromising performance.
Final Words
In our extremely competitive world, a slow website has no place at all; SSL offloading is a game-changer for faster and more secure information transmission. Businesses may enhance website speed, simplify SSL maintenance, and minimize the risk of security breaches by outsourcing SSL processing to a dedicated device. With the increasing significance of SSL encryption, organizations cannot afford to ignore SSL offloading.
