Port 80 (HTTP) vs. Port 443 (HTTPS): Everything to Know About the Protocols

Strong security is the primary distinction between Port 80 and Port 443. While Port 443 allows encrypted connections, Port 80 offers unencrypted connections.
There needs to be clarity among many of you over these many ports. What comes to mind when you read about Port 80 vs. Port 443? Indeed, the differences between HTTP and HTTPS may be familiar to you. These two helpful ports will be covered in this post, along with instructions on activating them on various operating systems.
Separate protocols for plain and encrypted communication are HTTP and HTTPS. In contrast to HTTP (the insecure protocol), 95% of online traffic is served over HTTPS (the encrypted protocol), according to Google’s transparency report. Port is used to handle all online traffic, encrypted or not. While port 80 is frequently used for HTTP, port 443 is utilized for the HTTPS protocol.
The distinctions between HTTP (Port 80) and HTTPS (Port 443) will be discussed in this article.
What is a Port?
A port is a number that corresponds to a particular protocol. It is a network connection virtual communication endpoint. Software created to run on devices and establish connections via the internet uses ports. The port enables computers to discern between various types of traffic and choose what action to take with data received or supplied over the same network connection. Computers receive enormous amounts of data.
Different ports have different numbers allocated to them, such as ports 80, 443, 21, 22, 53, 123, 179, and so on.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) assigns these numbers, commonly called port numbers, to specific protocols or services.
For instance, secure HTTPS connections utilize port 443, whereas HTTP traffic typically uses port 80. Computers may efficiently handle and route data according to the desired protocol or service by employing distinct port numbers, which guarantees successful network connection.
What is Port 443?
A secure version of HTTP, HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), encrypts all data as it travels via port 443. This port establishes a secure connection between the browser and the webpage and relates to the TCP protocol.
RFC 1700 formally published HTTPS Port 443, which was requested by “Kipp E.B. Hickman.” Robust security is the primary distinction between Port 80 and Port 443.
While data communication in plain text is possible via Port 80, data transfer via a secured network is possible via Port 443. Should a user attempt to access a non-HTTPS website, they will receive an insecure warning. Before data transmission, network data packets are encrypted via port 443. The SSL protocol takes advantage of port 443 security.
The increasing amount of cyberattacks and data breaches, which have brought attention to the need for encryption in securing sensitive data, has caused this move towards HTTPS.
Furthermore, websites using HTTPS connections are now prioritized by popular browsers and search engines, encouraging website owners to use this secure protocol.
As to Google’s study, a secure HTTPS connection via Port 443 is used to access over 95% of websites due to the increased awareness among internet users about the safety of their shared data with websites.
What Does “HTTPS is Encrypted” Mean?
When anything is encrypted, it prevents someone using WireShark from sniffing out packets or listening to the port to identify the data being transferred.
A key is transferred when a session is started between a server and a node. Data is encrypted before it travels and decrypted at its destination using this key.
Asymmetric encryption is used for this operation, requiring a public and private key. If someone needs to transact business with the server, they can have the public key kept on the server.
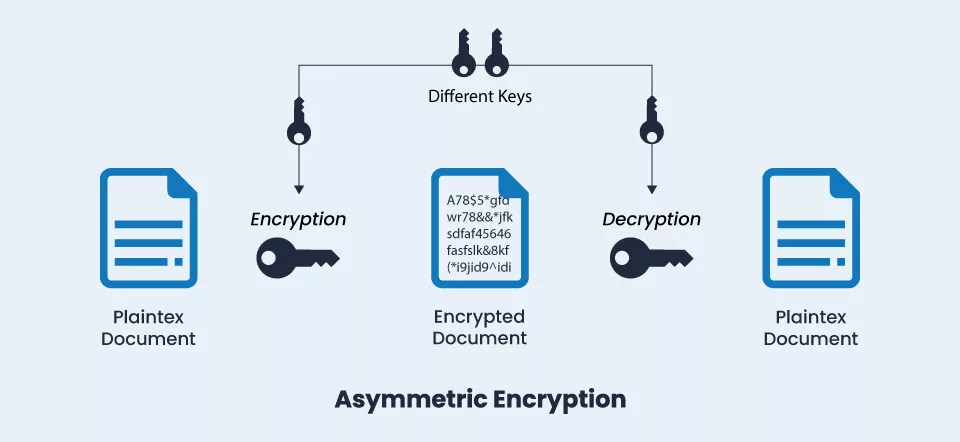
Consider it comparable to a safe. Anyone with the public key can lock and place a message inside the safe. But only the owner of the private key can open it. That is the way asymmetric encryption functions and, therefore, does HTTPS.
What is Port 80?
HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) connections utilise port 80 by default. It is a well-known and often utilized port worldwide. Tim Berners-Lee established port 80 in the HTTP 0.9 specification in 1991.
According to the paper, Port 80 is the default when no port is defined for an HTTP connection. You may access the World Wide Web (WWW) with it. This port allows a user to connect to websites accessible over the internet. It indicates that this port is used for unencoded data transfer between the user’s browser and the server. TCP (Transfer Control Protocol), a protocol used for data transfer, is related to this port.
Website browsing is made possible by the widespread acceptance of port 80 as the standard port for HTTP communication. Smooth and fast communication between the user’s browser and the server is made possible by the TCP/IP stack, which guarantees the reliable transfer of data packets across this port. Port 80 is also necessary for the exchange of unencrypted data, making it necessary to access various internet sites.
Why Use Port 80?
Port 80 is helpful for many purposes. Receiving traffic from the internet is the leading cause. Software developers may test the functioning of websites using port 80 without worrying about the intricacies of encryption. Load balancers can utilize port 80. The load balancers will use port 80 to receive traffic, which will then be divided across the shared servers.
There is a significant warning regarding port 80: do not use it on publicly accessible websites. Your site will appear lower in Google search results due to the impact on your SEO rating.
Redirecting an unencrypted URL to an encrypted one on port 443 is the last purpose for port 80.
Port 443 vs. Port 80: Major Difference to Know
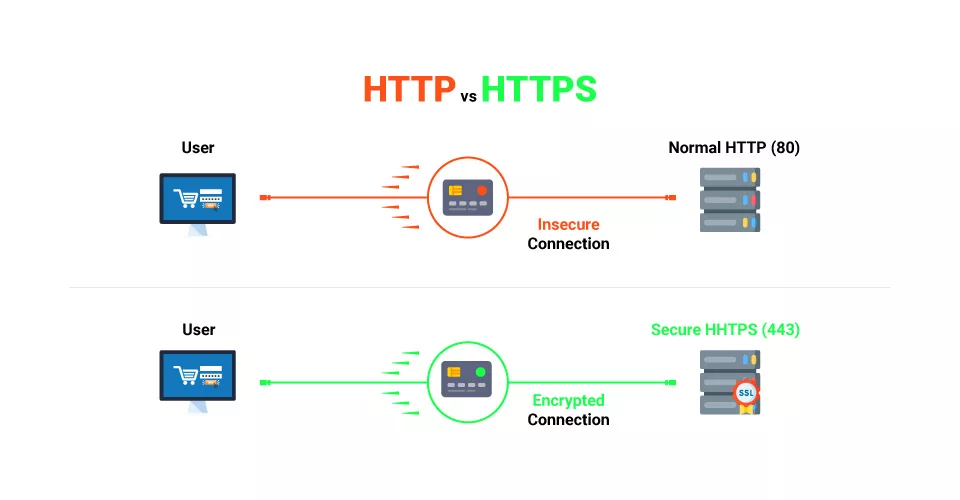
The critical distinction between port 80 and port 443 is that the former is unencrypted, while the latter is. Since HTTP is an unsecured transmission protocol used to get online pages, port 80 is, by default, unencrypted. Because port 443 employs HTTPS—a secure version of port 80—it is safe because it accomplishes the same goals.
What Makes Port 80 Different from Port 443?
As previously mentioned, the primary distinction between ports 80 and 443 is that the latter is encrypted while the former is not.
- Another significant distinction is that each sends packets using a different transfer mechanism. HTTPS uses TLS, a secure variant of TCP, while HTTP utilizes TCP. Considering everything, are port 80 and port 443 equivalent? In a word, sure — but allow me to clarify.
- While Port 80 permits data transfer in plain text, Port 443 allows data transmission via a protected network. Any attempt by the user to visit a non-HTTPS web page will result in an insecure warning.
- When the HTTPS protocol is enabled on port 443, all data transferred between the browser and the server is encrypted. Still, when the HTTP protocol is enabled on port 80, information is transferred between the browser and the server in plain text.
- Due to security concerns, nearly all browsers have switched to HTTPS, making HTTP obsolete. Google launched “HTTPS Everywhere” to improve web security.
- While sniffing the data on port 443 is challenging, attackers can readily sniff current conversations on port 80.
- HTTPS was published in 1994 RFC 1700, although port 80 entered into force in 1991 and was documented in the HTTP 0.9 specification.
- When consumers visit an HTTP webpage, their browser will provide a warning; however, HTTPS-enabled webpages do not issue any warnings.
Recommended Read: What is Port 443? How Does it Works to Provide Security?
Security Vulnerabilities in Ports 80 and 443
Examining vulnerabilities in security is a good idea if you want to employ a technology. Even though port 80 and port 443 are widely used nowadays, there are still vulnerabilities that need to be considered.
Security Concerns/Vulnerabilities with HTTPS (Port 443):
Even while HTTPS provides its users with high security, there are still specific safety measures to consider. When utilizing HTTPS, keep the following four weaknesses in mind:
SSL/TLS Certificates that are Expired or Invalid:
Any expired certificate raises the risk of data interception and a general decline in the certificate holder’s reputation. Someone may lapse somewhere if they are unable to maintain their current certificates. Renew your SSL/TLS Certificate at Cheapest Cost!
SSL Stripping:
An attacker could try to convert the HTTPS connection back to HTTP, allowing them to decode the data.
Man-in-the-Middle (MiTM) Attacks:
To steal data, a hacker can intercept it by pretending to be an intermediate website. If the certificate has expired, this process is straightforward.
Unsecure Redirects:
Many websites will instantly reroute an HTTP site to an HTTPS address. Incorrect execution might allow a hostile actor to take advantage of the weakness and intercept data.
Security Concerns/Vulnerabilities with HTTP (Port 80)
Since HTTP is not secure, there are several factors to take into account when using it, such as:
Data Tampering:
Since the information is in plain text, an evil actor can intercept and alter it before reaching its intended location.
Injection Attacks:
When a line is hazardous cross-site scripting is much simpler. This is so because HTTPS verifies that data packages are arriving from the intended origin, something HTTP needs to accomplish.
Content Injection:
By intercepting and manipulating packets, a hacker can inject CSS or HTML into your web browser.
Risk of public Wi-Fi:
In a public place, a malicious party can access both your data and that of others.
Conclusion
The TCP protocol allows an HTTP connection on port 80. Due to this port’s unencrypted connection between the web browser and the web servers, sensitive user data is left vulnerable to hackers and might result in serious data misuse.
Encrypted connection using HTTPS Port 443 ensures that no data breach can see the data because it is not readable by the web browser. For this reason, a secure HTTPS Port 443 connection is unquestionably preferable to an insecure HTTP Port 80 connection when accessing the web.
FAQ’s
What distinguishes HTTPS 80 from HTTPS 443?
Most websites nowadays utilize HTTPS, a port 443-based, more secure variant of the HTTP protocol. While Port 80 permits data transfer in plain text, Port 443 allows data transmission over an encrypted network.
What distinguishes HTTP and HTTPS ports from one another?
HTTPS is secure, whereas HTTP is not. HTTPS utilizes port 443; HTTP provides data on port 80. While HTTPS functions at the transport layer, HTTP runs at the application layer. While HTTPS requires an SSL certificate signed by a CA, HTTP requires no SSL certificates.
What is the Purpose of Port 443?
Because port 443 is intended explicitly for HTTPS services, it is the default port for HTTPS (encrypted) traffic. All secure transactions use port 443, also known as HTTPS port 443. It may surprise you that port 443 is used for secure transfers on over 95% of protected websites.
Does Port 8080 mean Port 80?
This port is a well-liked substitute for port 80 for providing online services. “8080” was selected because it is “two 80s” and is above the range of well-known, limited-service ports.
Which Three Kinds of Port Numbers are there?
Three ranges comprise the port numbers:
Renowned ports. The ports numbered 0 through 1,023. Registered ports are the most well-known. The registered ports from 1,024 to 49,151 are either private or dynamic. The ports numbered 49,152 through 65,535 are dynamic and private ones.
How to Find Blocked Port 80 and Port 443?
Determine the cause of the Windows port 80/443, preventing Qlik services from beginning.
Proceed to run the following commands at the Command Prompt (cmd.exe):
Using the generated PID, locate the task name in step two: jobsvc /FI /tasklist “PID eq 37400”
The job’s name blocking your port should appear in the output.

