PKI Certificate Management: Avoid Common Pitfalls & Embrace Best Practices

What is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)?
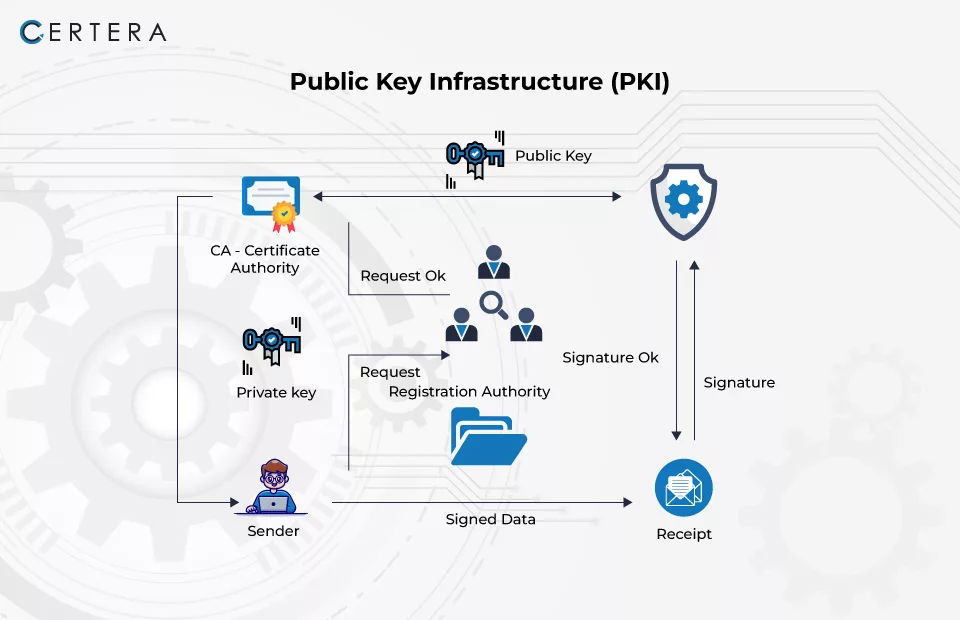
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a complex set of hardware, software, policies, and procedures that are used to create, manage, and store digital certificates and keys in a secure way.
It serves as the basis of secure communication and authentication methods in digital spaces like the Internet and private networks.
Fundamentally, PKI is based on a cryptographic technique known as public-key cryptography. In this system, each entity (such as a user, device, or server) possesses a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key and a private key.
The public key is disseminated and can be freely made available to everybody, whereas the secret key is known only to the owner and has to be kept secret.
What is PKI Management?
PKI Management (Public Key Infrastructure Management) is a general term for a system of sets of processes, procedures, and technologies that are used to administer PKI completely.
It creates a basis for the safe transfer of information, data transactions, and verifications within a digital environment. In order to ensure the correct work of the PKI ecosystem as well as its safety and reliability, PKI Management considers its principal elements.
Recommended: How Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Works to Keep Your Data Secure?
First of all, it includes the careful process of key pair generation and allotment management. This involves the resilience of the generation, distribution, and storage of public and private keys for different entities that are party to the PKI, including individuals, gadgets, and servers.
Proper key management should include the generation of cryptographic keys securely and the correction of access to authorized parties.
Lifecycle Certificate management is a decisive element in PKI management as well. The scope includes managing the issuance and renewal of digital certificates, revoking them and determination of their expiration lifetimes.
Recommended: Public Key Infrastructure Trends and Predictions for 2024
Avoiding fraud and maintaining the accuracy of the certificates all through the desired duration demands that their lifecycle is effectively managed from their issuance to their expiry.
It contains certificate distribution and enrollment processes, among others. It refers to the authentication, verification, and issuing of digital certificates to users and devices that seek authorization for resources featured in the PKI domain.
Enrollment processes for certificates and issuance are designed to verify the identity of the certificate seeker and to make sure the certificates are to be issued in a secure manner.
Consequently, PKI Management components such as the certificate revocation and renewal mechanism need to be in place.
In instances of key compromise, misuse, or if certificates were to be sent to a different host then they will need to be rescinded and new certificates issued.
Furthermore, mechanisms for validating certificate renewals are a valued element that allows for certificates to remain relevant and secure after expiry hours.
As part of PKI Management policy compliance management is included. For this, you should design and implement statutes, instruction policies, and control measures for PKI work.
Administrators of the organization specify the policies, certificate practice statements, and security controls to make sure that PKI and its services comply with industry and organizational regulations.
Recommended: What is Cryptographic Failure? Real-life Examples, Prevention, Mitigation
Moreover, key management facilities are available for backup and recovery of keys. In case of the theft or damage of cryptographic keys, the key escrow mechanisms store keys in secrecy, and authorized parties can request the recovery of the keys when necessary. This guarantees the data utility and the trust of the encrypted services or data sources.
Common Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Pitfalls
PKI usage vulnerability factors include an organization’s struggle with managing their PKI flows and machine identities, inherent security problems between machines and certificate authorities, and the on-premises private certificate authority security risks.
This factor, the involvement of multilateral actors or a non-governmental organization, can result in security vulnerabilities and impurities in the operation. Some common pitfalls are:
Management Challenges:
However, company-wide management of PKI and machine identities, even in the largest of organizations, tend to be complex.
This multiplicity of details can result in inadvertent misconfigurations, certificate expirations, and other operational complications that can make it hard to keep a functional and secure PKI.
Security Vulnerabilities:
Incomplete PKI coverage induces shortcomings, which are the possibility of private keys being accessed illegally, certificates being improperly issued, and encrypted protocols becoming weak.
These vulnerabilities may be those of data breaches and the overall security as such.
On-Premises Risks:
On-premise Alternatives Like MS-CA or PrimeKy EJBCA can come with performance, maintenance, scalability, and reliability hazards.
Problems occur with internal PKI systems which make the certification of use cases become limited and may cause the gaps in security.
Compliance Concerns:
Refusal to implement compliance norms in the field of PKI management may end up with legal troubles and reputational problems for the organization.
Organizations are mandated to ensure their PKI practices are in line with applicable data protection and security provisions.
Operational Disruptions:
Incidences of PKI management inefficiency can cause different painful outcomes of service disruption, failing communications, and data breaches.
These turbulences can cause a multitude of financial and operational abnormalities the companies should be ready to face.
Top PKI Deployment Mistakes
The top PKI deployment mistakes include:
Misinterpretation of Baseline Requirements (BRs):
Certificate failures are triggered mostly by CAs’ mistakes:- BRs are standards set on the web by operators of PKI.
Operators mess up the setting of BRs. Even though the issue of BRs infringement is only observed in 57% of the real-world incidents.
Lack of Proper Auditing:
Systematic failures in organizational design, business operations, individual operator mistakes, and unintendedly carelessly accuracy check are the main cause of such failures in PKI
On-Premises Private PKI Risks:
IT corporations that host their own Certificate Authorities, like Microsoft CA or PrimeKey EJBCA, can have issues of maintenance, scalability, and reliability.
Inconsistencies of on-premises PKI can be a failure in issuance of certificates internally and this may lead to (security gap).
Inadequate Planning of Certificate Templates:
Those who build AD CS (Active Directory Certificate Services) Certificate Templates often fail to plan adequately for the complexities that arise as a result of some misconfigured templates being the molds used to pattern others. This may therefore raise the network to security violation as a result of severe access limitations.
Lack of Certificate Delivery Mechanisms:
AD CS doesn’t feature any certificate delivery features that might increase the IT department’s burden and thus, the smooth running of the environment.
These security issues could be prevented with cloud-based services like SecureW2 that provide self-serving clients for many OS and Gateway APIs for integration in MDM as well as IoT applications systems.
Understaffing:
Typically, in-house teams are not provided with appropriate training to know how to manage a certificate authority since they do not deal with such matters often.
On account of these arguments the enterprises that would run their own PKIs come to the decision to avoid staging the very PKI and prefer to contract a managed PKI provider managing it.
How to Overcome and Avoid PKI Mistakes?
To overcome and avoid PKI management mistakes, organizations should implement the following strategies based on the insights from the provided sources:
In order to rectify and avert PKI pitfalls, organizations are advised on the application of the following strategies which sort them out based on the sources provided.
Proper PKI Management:
Set thresholds which can’t cross over to the security altars nor to the rights of the humans, allot funds adequately and immerse yourself in regular auditing for the well managed PKI security.
Certificate Lifecycle Management:
Assign the certificates machine to run a certificate management system, check the mitigation of certificates expiration, do not reuse certificates across the devices and by these the issues on outages and security threats would be overcome.
Security Measures:
Secure your private key, install up-dated security software promptly, and make use of safe key registration to be safe from security attacks and intrusion intent.
Governance and Policy Enforcement:
Keep the guidelines, ensure that policy is ever followed, and single page response to any ISSUE that sounds the warning alarm to prevent possible problems amid the implementation of PKI.
Training and Awareness:
Teach the developers and system administrators the protection foundation and the proper usage of the secure protocols security but with a particular focus on the PKI management to maintain the high security posture.
PKI Best Practices
Best practices of PKI (public key infrastructure) could consist of key sections such as planning and design, key and certificate lifecycles, private key protection, auditing the CA, root certificate, internal security, cryptographic agility, secure storage of keys, automated key rotations, and periodic audits.
In addition to that, such measures need to be incorporated into the package in order to ensure the safety of the PKI management, and also the effectiveness, to prevent the creativity of security flaws and loyalty with the security policy and the level of fairness that are desired.
Here are some Best Practices:
Design and Planning
Regarding the construction and planning procedures of PKI system architecture, the following items need to be taken into consideration:
The algorithm selection, key sizes for proper functioning and usage and the development of policies concerning certificates issuance, revocation and renewal.
The stage follows too which characterizes PKI functionality area, systems and applications investigation that may generate certificates as well as security certificates generation listing.
Key and Certificate Lifecycle Management
The administrative matters around the public key infrastructure also covers the entire management of key and certificate life which means issuance and renewal on top of deleting keys for every copy when you like.
Certificate authority (CA) has strong policies, which include branding, tailor-made and specialized certificates, stringent key storage policies, and regulation and renewal of certificates and computer naming.
Private Key Protection
For this, high-level security encryption and accompanied safe storage methods have to be used to protect the private keys. HSMs and secure key storage devices may be parts of such security efforts. And they may also rely on the use of access controls and stringent key management plans.
Certificate Authority Audits
Certificate authority audits need to be carried out on a regular basis to ensure that every certificate authority is following the security rules and looking for the security weaknesses.
In this regard, the periodical evaluation of security assessments together with log access reviews is of critical importance and accompanying the assistant authorities in meeting all of their configuration procedures.
Root Protection
Backup’s network backup mechanism includes the implementation of rigid access control. Making sure that the roots are secured and reviewing the configuration of the roots frequently are also the mechanisms that Backup employs.
Internal Security
PKI governance is connected to addressing the internal security risks such as what is referred to as Insider threats, other forms of attack and Social engineering.
The system provides for instance, license management, authentication verification if needed and secure keys.
Cryptographic Agility
The PKI system must focus on advancing cryptographic agility that includes the ability to effortlessly swap between various encryption algorithms and key sizes.
This is critical in ensuring the present day security of the homeland against new developments of cryptanalysis and threat advances.
Secure Key Storage
The private keys of the users shall be stored securely, preferably by using HSMs(hardware security modules) or other hardware secure storage.
This performs the role of resisting the chance of shared key loss due to attacks of unlawful entry, theft, or abrupt loss.
Automated Key Rotation
Key rotation of the automation also implies that private keys and the digital certificates that go along with them have to be changed periodically.
This is mostly for minimizing the risk of a compromise and guarantees that the PKI stays secure all along.
Periodic Audits
Continuous auditing processes of PKI elements and techniques are necessary to make sure security rules are enforced and to detect in advance any potential flaws.
This includes looking into the access logs, noticing in general suspicious behavior, and maintaining all PKI components as being properly configured and maintained.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricate landscape of PKI Certificate Management can be challenging, but with the right tools and practices in place, you can mitigate the risks associated with PKI Mistakes.
Certera offers a comprehensive solution to streamline PKI Management, helping you avoid the pitfalls of PKI Certificate Management Mistakes.
Embrace best practices, empower your security infrastructure, and safeguard your organization’s digital assets effectively!
