What is HTTPS? Why it’s Important for Website and SEO

What is Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS)?
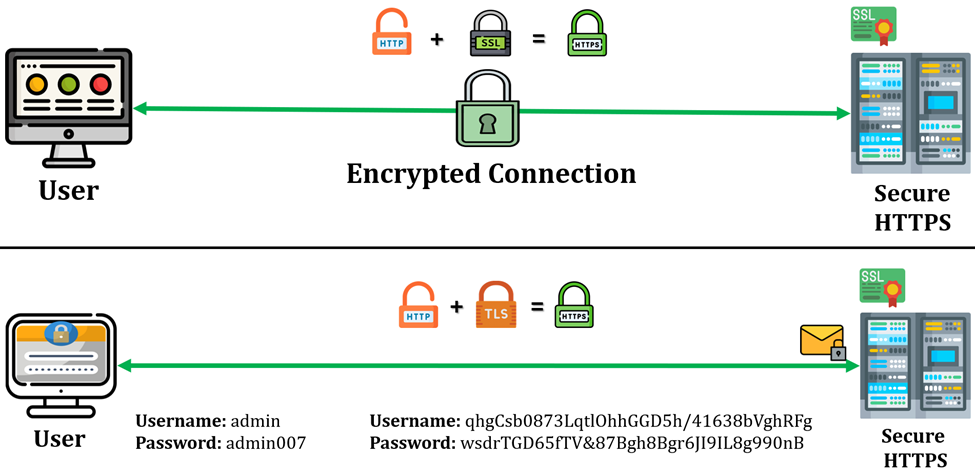
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a variant of HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), the standard technique for transmitting data via the web browser to the website’s server. HTTPS maintains the secrecy of the information by coding the communication between the browser and the website’s server.
The encryption used for these routers, therefore, provides privacy and integrity of the transmitted data from being spied upon, altered, and stolen.
HTTP vs. HTTPS: Difference to Know
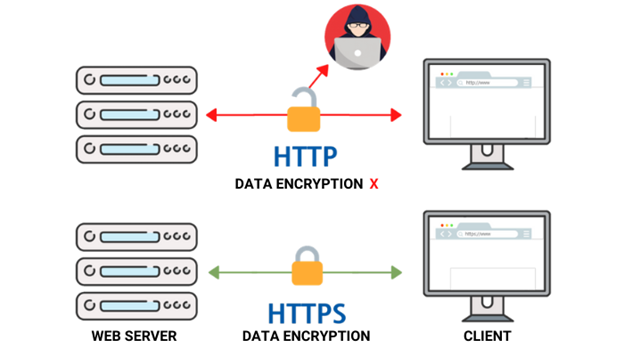
Understand the major difference between HTTP and HTTP(s)
| Feature | HTTP | HTTPS |
| Protocol | Hypertext Transfer Protocol | Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure |
| Security | Not secure – data transmitted in plain | Secure – data encrypted using SSL/TLS |
| Data Encryption | No encryption | Encryption ensures data confidentiality |
| Data Integrity | Data integrity not guaranteed | Data integrity ensured |
| Authentication | No authentication | Server authentication provided |
| URL Prefix | http:// | https:// |
| Port | 80 | The browser displays padlock icon |
| Browser Warning | No browser warning | Browser displays padlock icon |
| SEO Impact | May negatively impact SEO rankings | Positively affects SEO rankings |
| Website Trust | Lower level of trust from users | Higher level of trust from users |
| Regulatory Compliance | May not comply with data protection regulations | Helps meet regulatory requirements |
The Importance of HTTPS
HTTPS, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, is of pivotal importance for securing the data transmitted via the internet. It is an extension of HTTP, the protocol for switching web pages and other content on the Internet.
HTTPS adds an additional security layer by encrypting data between user browsers and website servers, making the data transfer secure, confidential, intact, and authentic.
1. Data Security
One of HTTPS’s major goals is to guarantee the security of the data communicated between the user’s browser and the server. HTTPS secures your data using SSL/TLS encryption protocols, which make the transmission unreadable to unapproved parties who may tap it.
Recommended: What is Port 443? Detailed Guide on HTTPS Port 443
Encryption of this kind keeps hackers, data thieves, and producers of tempered data away from the platform. The channel keeps the login details, personal records, and transactions in the list.
2. Protection Against Cyber Threats
Currently, the digital world is the main arena for cyberspace violations, ranging from data breaches and identity theft to phishing. HTTPS, which constitutes one of the ways to mitigate these risks through the provision of a secure channel for data transmission, is no exception.
Recommended: What Digital Threats Can SSL Prevent?
The cryptography used by HTTPS significantly reduces the level of malicious activity, as there are fewer chances of data interception, unauthorized access, and manipulation. This increases cybersecurity posture and protects user data privacy.
3. User Trust and Confidence
Websites that use HTTPS display trust and confidence to users so that they feel reassured. When visitors see the padlock icon and “https://” and type a domain name into the browser address bar, the very presence of the “HTTPS” or “Secure” word indicates that their connection with the website is secure.
Recommended: Facts, Trends, and Statistics for SSL
This guarantee is a step towards instilling confidence in the site, which has a positive impact on users’ perception of the site as legitimate and reliable. Users will be able to interact with the content and share sensitive information privately.
4. Compliance with Regulations
Numerous regulatory frameworks and industry standards incorporate the implementation of data and privacy protection into their requirements.
Cases of this type include the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), the PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), and the HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
HTTPS is crucial for complying with these regulations; it ensures that data transmission is secure and that it is protected against unauthorized access and data breaches.
5. Improved Search Engine Ranking
Search engines like Google display HTTPS websites at the top of their results over non-secure HTTP sites that display downgraded search rankings. Sites that implement the HTTPS version may yield better search engine ranking, more organic traffic, and more clicks over websites that haven’t done that yet.
Google has revealed its secret: HTTPS is a ranking signal, and sites that use it will be given a visible hip boost that might increase their visibility online.
6. Prevention of Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
HTTPS builds up a defense against man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, where an intruder steals and replaces the information being transferred between the browser and the server. Encrypting the data is the responsibility of HTTPS, thanks to which the transmitted information remains confidential and inviolable, protecting the safety from MITM attacks and from unauthorized modifications of the data.
7. Enhanced Browser Security Features
Today’s popular web browser features give extra protection for https-enabled sites, whether it is a warning system or security features. On the other hand, http sites are still recommended.
Browsers can initiate a pop-up for users to enter the HTTPS website or not. In some cases, they can even completely forbid access to non-secure sites, forwarding users to HTTPS sites that are safer to surf.
This way, both safeguard HTTPS as a standard and enable website owners to adopt HTTPS in their websites to protect against browsers’ security inquiries and keep the trust of users.
8. Protection Against Content Injection
HTTPS minimizes content injection attacks’ chance, in which intruders inject malicious code or advertisements into unsecured web pages.
HTTPS secures the encrypted connection, so the content remains unchanged, and there is little chance of it being compromised during transmission to the receiver. This helps protect the website’s content as well.
9. Mobile Compatibility
As demand for mobile use of the Internet increases, HTTPS is used to guarantee the requirements of security and compatibility whilst a person accesses it from various platforms and devices.
Browsers embedded in mobiles make a statement by featuring HTTPS-enabled first, and those that are not are displayed with a warning that users will probably choose to navigate to other secure sites.
HTTPS implementation enables a user to enjoy browsing websites with full confidence since it provides a consistent and secure experience. As a result, a user definitely develops loyalty and trust to any particular site.
10. Future-Proofing
Internet security threats will always continue to emerge, serving as ideal cover for upcoming vulnerabilities and more advanced attack vectors.
Therefore, HTTPS will continue to be an integral part of the online security ecosystem, whose role will mostly be that of a shield against incoming cyber attackers.
HTTPS servers illustrate foresight by coming up with solutions to which the constantly morphing cyber threats keep responding, and still, the websites stay resilient to their attacks. Thus, they will provide future protection to the data and users.
Moreover, the implementation of HTTPS technologies of the emerging generation and TLS 1.3, among the best security methods, are other effective measures that double up the security of HTTPS websites, resisting even the most advanced attacks and flaws.
How Does it Work?
HTTPS implementation begins with the SSL/TLS handshake process, which is responsible for establishing a secure connection. During this message exchange, the web browser (client) and the web server negotiate the parameters to be used during the connection process security.
Recommended: How Does SSL Certificate/HTTPS Work?
The client kicks off the handshake by sending a “Client Hello” message to the server, identifying its support for SSL/TLS, specifying which cryptography algorithms or parameters are to be used.
The server answers with a “Server Hello” indication that it received the client’s requests and the protocol to implement will be chosen suitably depending on the TLS/SSL version and cipher suite.
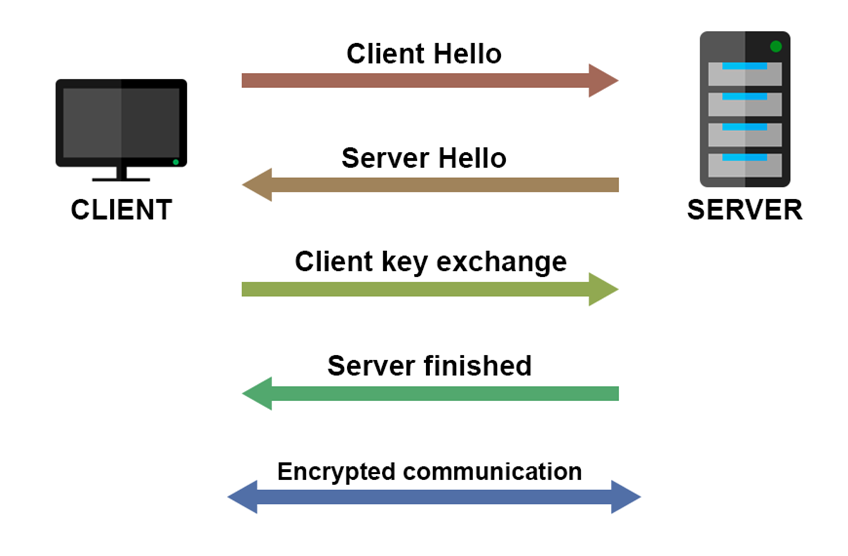
In its turn, the server hands over its digital certificate to the customer. This certificate has the server’s public key and some additional information to verify the validity of the certificate. It is usually issued by a trusted certificate authority (CA).
The client verifies the authority of the certificate issuer and checks whether that certificate is accurate and legitimate. The point of the certificate is that it is valid and reliable; if so, the procedure continues to the next step.
The server’s public key, recognized by the certificate, is used by the client to create a symmetric encryption key for the session. This particular key is important in setting up an encrypted channel of communication between the client and server by providing the encryption and decryption needed for data exchange.
Clients will pass the previous symmetric key (which needs to be encrypted) to the server via the public key encryption method.
After getting the symmetric key’s encrypted version from the server, the client can use it with its private key. Both the client and server now possess this symmetric encryption key, which will be used to make that secure channel work as a secure medium of data transmission.
During the process, the servers and clients are the only ones who can decrypt the data being exchanged during the session; thus, confidentiality is assured.
After the connection is established, the data transfer is protected using symmetric cryptographic algorithms based on AES (Advanced Encryption Standard).
Moreover, SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256) is deployed to generate a message digest for data containing data packets to maintain data integrity during transmission. This, in turn, results in data remaining the same and unchanged during transmission protection against tampering and manipulation by cybercriminals.
HTTPS, in addition, facilitates mechanisms of authentication to ensure the identities of the parties can indeed be verified, thus making the link between the communicating parties impossible for Man-in-the-Middle attacks.
The certificate signing process via client machine server digital certificates authenticates the server’s identity. Thus, the client can recognize the server’s sophistication.
Web browsers display visual indicators, such as a padlock icon and “https://” prefix within the URL, to indicate that these connections are secure with the HTTPS protocol. These indicators are suitable for earning the user’s trust that his/her connection to the website is secure and data is safe from unauthorized sources.
How to Check SSL Certificates?
Customers can find out if a website has a secure connection via SSL encryption by following the steps. Initially, look at the address bar of your browser for the padlock icon.
This symbol represents the fact that the website is secured through an SSL encryption method using the HTTPS protocol. By clicking on the padlock icon, people see even more information, usually labeled “Connection is secure.” In most cases, this brings the user to the SSL protocol certificate.
Recommended: SSL Certificate Checker Free Tool – Check The Installation Status of Your SSL Certificate Online
As the “Connection is secure” icon is clicked, the user is opened to a window or box that has all the information of the SSL certificate. This information involves the issuing CA name or the CA issuing date, the expiration date of the certificate, and the validity period of the certificate. Users can check this data to ensure that the certification is original and representative.
People who desire a more in-depth analysis of the SSL certificate can follow the prompt, which will most probably be labeled “Certificate is valid” or in a similar language.
This redirects the users to a page that has a more in-depth description of the certificate by clicking on these links. Here is where the users peel off the certificate to get to the details, which clearly indicate the general specs and parameters of the certificates.
Users will also be able to view things like a statement directly from the issuer or a link associated with the SSL certificate. This link will lead users to the particular webpage or platform involved in the Certificate Authority of issuance.
The user will have access to the additional resources and information about the SSL certificate, and as a result, accuracy and reliability will be ensured.
Importance of HTTPS for SEO
Site owners must know that adopting HTTPS is not optional but is an essential part of any SEO strategy in today’s digital environment.
HTTPS, the secure form of HTTP protocol that is used to transmit data between a web browser and the server, stands as an abbreviation of Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. Here’s why HTTPS is crucial for SEO:
Security and Data Protection:
HTTPS implements encryption over the data transferred from a user’s browser to the website’s server, which prevents third parties from manipulating or stealing sensitive information.
Such data security is, therefore, very important because it assures users of their login credentials, payment products, and personal information by making the website a place that is recognized and trusted by users. Search engines rank sites with secure connections as their top priority to preserve customer privacy.
Ranking Signal:
The most used search engine is Google, which gives priority to HTTPS within its search algorithm. Those search engines that are HTTPS sites rank higher than the HTTP ones that end up at the bottom of the search engine results pages.
Website hacking poses serious threats to people’s online data as well as the trust in the browsing experience. This is why Google focuses on the security of websites to allow a positive and trusted browsing experience. In conclusion, website migration to HTTPS can contribute to better search engine visibility and further organic traffic for those sites.
Browser Warnings:
Browsers such as Google Chrome, the Firefox extension, and Safari will display warnings to users when they are visiting non-HTTPS websites. The warning banners are able to alert online users that there are security problems when they visit insecure websites and thus avoid further interaction with hazardous sites.
The drop in access may make it difficult to sustain a specific HTTPS website compared to the ones with it, which might lead to higher bounce rates and lower user engagement metrics and, as a result, affect their SEO performance.
Referral Data Integrity:
An HTTPS connection that redirects traffic to a non-HTTP website can encrypt referral information. It is this removal of the essential data and reduced traffic accuracy that makes the problem worse for website owners. Moving to HTTPS will allow websites to break referral data integrity, which is the basis for gaining those insights and improving SEO strategies in this way.
Mobile Optimization:
A mobile-friendly website is among the top elements that Google is using this time to assess the site’s ranking on its mobile search engine. Increasingly, mobile phones are being used by users.
Therefore, guaranteeing a safe browsing experience on all mobile devices becomes crucial. HTTPS is the factor that promotes mobile optimization as it supplies a safe connection for mobile devices and websites.
Mobile-compliant websites that make use of HTTPS are among the top preferred ones by the search engines and, thus, have a greater chance to rank in the top position of mobile search results and become a mobile-SEO-success story.
Trust and Credibility:
Sites that possess the padlock emblem and the ” https://” prefix in the URL create the feeling of an integrated security system, where users can be secure that their personal information is safe and confidential.
The visual fostering of HTTPS encryption results in an HTTP designation that further confirms the website’s integrity and credibility to site visitors and search engines.
Trustworthy websites are much more likely to get the backlinks of search engines, likes, and social shares, all of which lead to SEO performance improvement.
Conclusion
SSL certificates play a vital role not only in ensuring that end-users expectations of website security and trust are met but also in search engine optimization (SEO) purposes. By establishing HTTPS, websites can increase their credibility, secure user data, and rank higher on the SERPs.
Thus, website owners and managers should do everything possible to ensure their sites’ security by purchasing an SSL certificate and shifting to the HTTPS protocol. Place your SSL certificate investment as a priority today to secure your website and get the most out of the increased security, trust, and SEO success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is HTTPS important for SEO?
HTTPS is one reason it matters a lot for SEO, as it improves site safety, creates trust with users, and boosts their positioning in search engines.
Overlaying the information exchange happening from a browser to a website’s server with encryption, HTTPS protects the information from theft and inspires trust in users. Google HTTPS, the search engine, is used as a ranking factor, and secure websites rank a notch higher compared to insecure sites on search engine result pages (SERPs).
2. What is HTTPS, and Why is it Important for Web Security?
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a secure protocol used for communication between web browsers and web servers to send and receive data. It uses encryption methods, such as an SSL/TLS certificate, to ensure that the data is not interrupted in transit or modified on the fly.
HTTPS is the most important part of web safety because it ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of information transmitted on the web.
3. Why is HTTPS more Secure?
HTTPS is more secure than HTTP as it employs encryption mechanisms such as Secure Socket Layer/Transport Layer Security certificates to encrypt data flowing from the web browser to the website server, whereas HTTP does not use any security mechanism to protect data.
This approach makes data unreadable during the transmission, protecting it from interference and falsification by bad actors. Besides, HTTPS covers the validation of websites by SSL/TLS certificates brought by trusted certificate authorities, which decreases potential dangers such as phishing attacks and man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
