What are the Most Common SSL Certificate Errors? How to Fix It?
According to Forbes, there are 1.13 billion websites on the internet in 2023. But do you know how many of them use an SSL certificate? More than 46 million websites! And for every such user, an SSL certificate not trusted error is expected.
It indicates the connection to a website is not secure, which can cause concern. Fortunately, fixing this error can be straightforward. This guide explores resolving this error and ensuring your online browsing is safe and secure.
SSL certificates have become a critical part of online security and for good reason. SSL certificates lend credibility, making sites appear more trustworthy.
However, despite their importance, SSL certificate errors can occur and cause customers to lose trust in your site. In this post, we’ll dive into what SSL errors indicate and what could be causing them.
What are the Multiple Types of SSL Certificate Errors?
Several types of SSL certificate errors can occur on a website. Let’s explore some of the most common ones:
When your SSL Certificate Shows “Expired” Error:
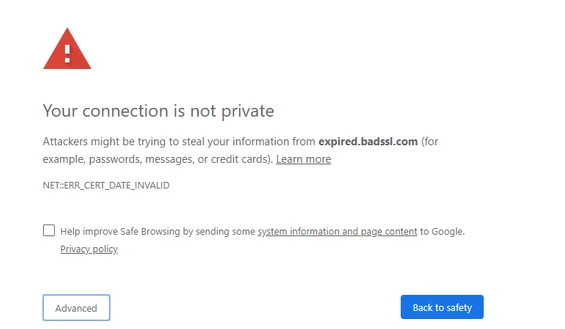
This error occurs when a website’s SSL certificate has expired. According to industry standards, SSL certificates have a maximum lifespan of 398 days, meaning they must be renewed or replaced at least once every two years to maintain secure communication.
When your SSL Certificate gets a “Not Trusted” Error:
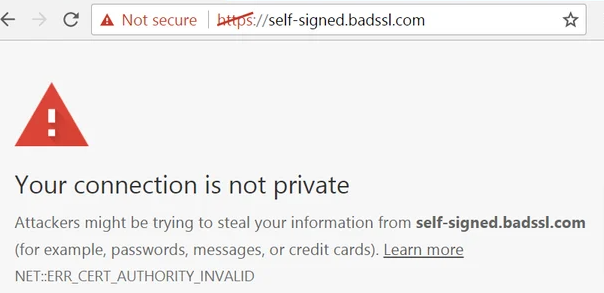
This error occurs when the SSL certificate is signed or approved by a certificate authority (CA) that the visitor’s browser does not trust. It can happen if the CA is off the browser’s list of trusted certificate providers or if the server itself issued the certificate a self-signed certificate.
When your name gets “Mismatched” Error:
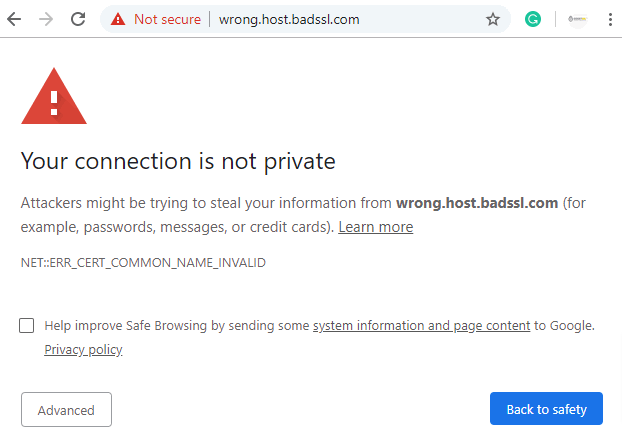
This error indicates that the domain name mentioned in the SSL certificate does not match the URL typed into the browser. For example, if the certificate is registered for “[www.yoursite.com](http://www.yoursite.com),” accessing the site using “<https://yoursite.com>” will result in an SSL certificate name error.
“Revoking” your SSL Certificate Error:
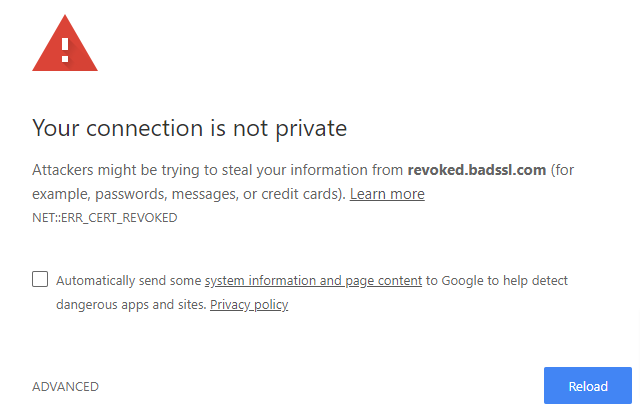
If the certificate authority cancels or revokes a website’s SSL certificate, the browser will display an SSL certificate revoked error. This could happen if the website obtained the certificate with false credentials, compromised key, or issued an incorrect key.
When your Content gets “Mixed” Error:
When a secure page (loaded with HTTPS in the address bar) contains elements (such as images, iframes, Flash animations, or snippets of JavaScript) that are loaded from an insecure page (loaded with HTTP in the address bar), a mixed content error occurs.
Browsers display an error message instead of loading the page to ensure user data security.
It is essential to promptly address SSL certificate errors to ensure a website’s security and trustworthiness.
How to Remove Generic SSL Protocol Error?
Resolving this error can be a complex task due to various potential causes.
- Some of these causes include an SSL certificate that is improperly formatted, making it difficult for the browser to parse.
- Another possibility is a certificate that must be correctly installed on the server.
- A faulty, unverified, or lack of digital signature can also contribute to this issue.
- Using an outdated encryption algorithm is another factor that may lead to this error.
- It is also worth considering whether a firewall or other security software interferes with SSL protection.
- Lastly, a problem in the certificate’s chain of trust, which refers to the series of certifications that compose your site’s SSL encryption, can also be a culprit.
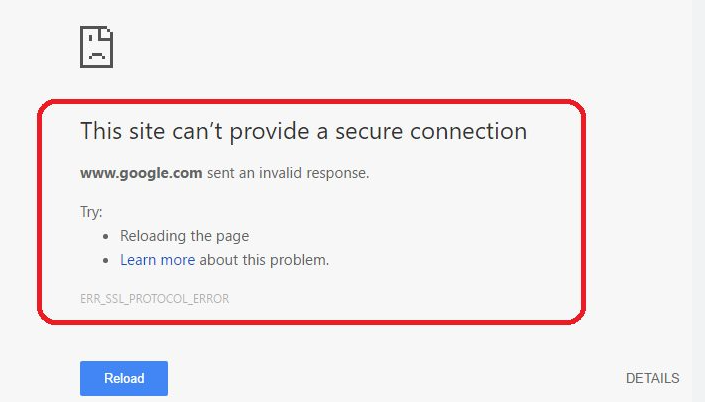
Once you find the culprit, consider removing it permanently or searching for an alternative with similar functionality but better compatibility.

How can I Renew my existing SSL certificates?
If your website’s SSL certificate has expired, it is imperative to renew it promptly to ensure that your site remains secure. While the specific details of the renewal process may vary based on the web host or Certificate Authority (CA) you are using; the fundamental steps remain the same.
Renew your SSL certificate by generating Certificate Signing Request (CSR), which will need to be authenticated by the CA. Once the authentication process is complete, you can activate your renewed SSL certificate, after which you must install it on your server to complete the renewal process.
It is critical to perform this renewal process efficiently to eliminate the risk of any security breaches due to an expired SSL certificate. Therefore, it is crucial to stay vigilant and keep track of the expiration dates of any SSL certificates associated with your site, ensuring that you renew them promptly.
How to Install an Intermediate Certificate:
If you encounter an issue where your Certificate Authority (CA) is not trusted, installing an intermediate certificate on your web server may be possible. Intermediate certificates are crucial in helping browsers validate that a reputable root certification authority issued your website’s certificate.
Certain web hosting providers, like GoDaddy, may offer guidance on how to install intermediate certificates. It is advisable first to confirm if your web host provides the option or a tool to obtain an intermediate certificate.
If not, take a moment to review your website’s server and locate the instructions specific to your server setup. By following the appropriate instructions, you can ensure the successful installation of an intermediate certificate, thereby addressing the trust issue with your CA.
How to Get a Certificate Signing Request:
If you continually receive the certificate not trusted error, the certificate may need to be installed correctly.
In such cases, generating a new Certificate Signing Request (CSR) from your server can be a viable solution, followed by reissuing it from your dependable certificate provider.
- The initial steps for generating a new CSR may vary based on the server you are using. Therefore, it is recommended to consult the appropriate documentation or seek technical assistance to obtain an updated CSR.
- This approach has proven effective in rectifying any errors that may have arisen from the previous installation.
- Once the updated CSR has been obtained, you can reissue a new SSL certificate from your provider.
- By leveraging this process, you can minimize errors and ensure that the SSL certificate is installed correctly, resolving the certificate not trusted error.
How can you use Online Tools to Solve the Problem?
To troubleshoot the SSL certificate error on your website, you should utilize online tools specifically created for this purpose. These tools can help identify and pinpoint the underlying problem causing the error.
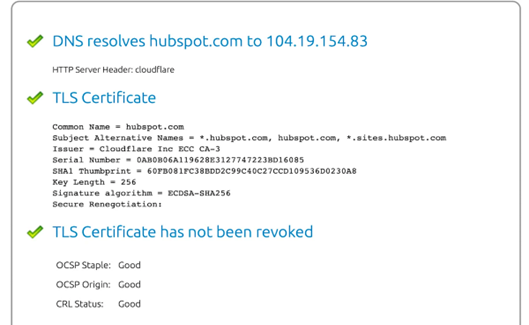
Several reliable options are available, such as SSL Checker, SSL Certificate Checker, or SSL Server Test. Using any of these tools can verify if an SSL certificate is installed correctly and has not expired. They can also check if the domain name is accurately listed on the certificate, among other relevant checks.
To utilize these tools, simply copy and paste your website’s address into the search bar provided by the selected tool. This will initiate the analysis and provide valuable insights to diagnose the SSL certificate error.
How can I Get a Unique IP Address?
If you encounter a name mismatch error, the root cause might be related to your IP address. When you enter your domain name in the browser, it initially connects to your site’s IP address before redirecting to your actual website. In most cases, each website has its unique IP address.
However, if you use a web hosting type other than dedicated hosting, your site might share an IP address with multiple other sites. It might lead to issues if websites still need an SSL certificate installed.
- When a browser encounters this scenario, it may struggle to determine which site to visit, resulting in a name mismatch error message. Thankfully, this issue can be resolved by upgrading to a dedicated IP address for your website.
- By obtaining a dedicated IP, you ensure your site has its unique IP address, eliminating the confusion caused by shared IP addresses.
- Upgrading to a dedicated IP address effectively resolves the name mismatch error and ensures a smoother browsing experience for your visitors.
Attempt to Modify all URLs to HTTPS
Suppose you encounter a mixed content error on any of your web pages. In that case, a practical approach is copying and pasting the URL into WhyNoPadLock.com to identify the insecure elements causing the issue.
Once you have identified these elements, you can edit the page’s source code and adjust the insecure elements’ URLs to HTTPS. This transition to HTTPS is essential to ensure your site is secure and users can browse it safely.
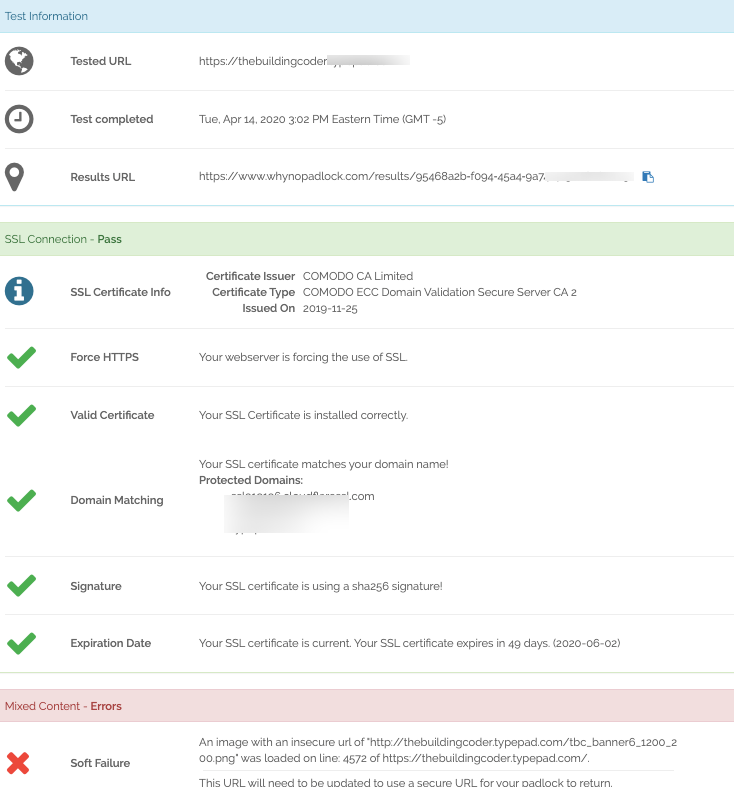
If you require additional support after reviewing the results, it may be time to contact your web hosting provider for further assistance. By working closely with your hosting provider, you can find a solution that ensures that your website is securely accessible to visitors and free from any mixed content errors.
How to Obtain a New Wildcard SSL Certificate?
If you still encounter a name mismatch error, consider obtaining a wildcard SSL certificate. This type of certificate offers the advantage of securing multiple subdomain names and your root domain. By obtaining a wildcard SSL certificate, you can address the issue of name mismatches and ensure a secure connection across various subdomains.
For instance, with a Multi-Domain SSL Certificate, you can encompass all of the following names under a single certificate:
- Mysite.com
- Mail.mysite.com
- social.mysite.com
- Blog.mysite.com
- Services.mysite.com
By procuring a wildcard SSL certificate, you can eliminate the name mismatch error and provide comprehensive security for your entire domain and its subdomains.
Process for Rectifying an Invalid SSL Certificate
There can be many reasons why an SSL certificate might need to be fixed. Regardless of the cause, website visitors will encounter a warning message in their browser, indicating the site is insecure. It has a detrimental impact on your reputation. Therefore, it is crucial to address the lack of encryption promptly.
If the troubleshooting methods mentioned earlier do not resolve the issue, we highly recommend contacting your hosting provider for further assistance.
They are experienced in dealing with similar problems and can provide valuable guidance. Consulting your hosting provider increases the chances of identifying and rectifying any issues related to your SSL certificate.
Remember, taking the necessary steps to ensure the security of your website is essential for maintaining a positive reputation and delivering a safe browsing experience for your visitors.
Its a Wrap!
The above solutions will serve you right for the SSL certificate, not trusted error. To sum up, it can be rectified by updating and correctly installing SSL certificates, verifying domain name matches, checking date and time settings, updating the operating system and browser, and seeking assistance from website administrators or support teams.
By implementing these solutions, you can ensure a secure and trusted browsing experience for yourself and your website visitors.
Buy Cheapest Wildcard SSL Certificate Starting @ Just $39.99/Year
