How to Tell If an Email Is Fake or Real?

With billions of emails received daily, it’s challenging to determine which emails are legitimate and which are illegitimate.
94% of workers require support and guidance in identifying the difference between genuine and fraudulent emails.
There are a few distinct signs that the email we got is fake. If we know these warning signs, we could prevent the consequences of falsified emails.
Do you need assistance to identify a fraudulent email from a legitimate one? Quickly, we’ll discuss it. But first, let’s think about how deeply email has embedded itself into our daily lives, personally and professionally.
Despite the ease that emails provide, there are certain dangers that we should all be aware of. As more people communicate through email, hackers are having an active day robbing individuals of their hard-earned money.
Emails are an especially appealing attack channel for criminals for several reasons:
- You could get a free or inexpensive email account.
- Creating an email account becomes simple for everyone.
- Emails reach quickly.
- Simultaneously forwarding multiple emails is simple.
- You can send and receive emails with an internet connection using laptops, tablets, and other mobile devices.
And if you believe you are too intelligent to fall for an email scam, rethink! As history has repeatedly shown, even the finest among us may fall prey to email scams. Seems absurd?
Well, that’s reality. Email fraud scams have victimized organizations, including Google, Sony, Upsher-Smith Laboratories, Facebook, and Ubiquity Networks. When significant companies encounter attacks, millions of dollars are lost.
However, Individuals and small-to-midsize organizations might lose hard-earned money stashed aside for unexpected expenses if we fall for a scam.
Everyone must understand how to identify fraudulent emails from an actual (legal) email.
This guide provides you with the information and tools you need to recognize and check the legitimacy of email addresses.
By developing your ability to recognize fraudulent emails, you can implement the necessary precautions to ensure that you communicate with trustworthy individuals and avoid becoming a victim of internet fraud.
Secure Email Communication with Trusted S/MIME (Email Signing Certificates ~ Starts at $9.49/yr
Ways to Detect Fraudulent Emails
Let’s look at six things you should know when determining whether an email is genuine or fake.
Double-check the Email Address’s Domain
Checking the hosted domain of a bogus email address is a popular detection method. Many fraudsters employ names that resemble popular websites like Google, Facebook, and Yahoo to deceive you into believing they are authentic.
You’ll frequently come across fraudulent emails with “from” addresses that resemble actual ones.
Consider Apple as an example. You will notice the email address is [email protected] if you get an email from Apple. To deceive the receiver, hackers would use similar email addresses like [email protected].
Alternatively, scammers could show you the genuine email address using blockers or spoofing software. This makes it considerably more challenging to determine whether the email is genuine. Any spelling errors in the email or suspicious-looking links are red flags.
Examine Email Headers
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are the three most widely used email security methods. These technologies make it easier for email users to determine if an email is coming from a legitimate sender or a fraudster.
Most well-known websites and companies correctly implement these three security measures, which enable your mail client to identify and reject bogus emails. It’s essential to remember that not all businesses will implement or use these technologies correctly.
Any suspicious email can be verified secure by selecting Show Original (or a similar option) from the three dots in the top-right corner. Each security check and a passing or failing grade for the email will be seen here.
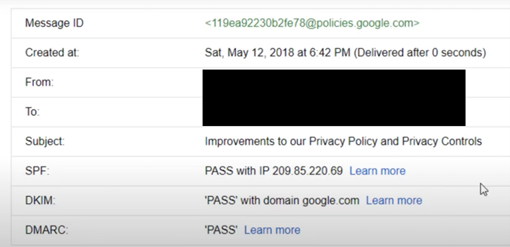
Even while the status can’t tell you whether an email is authentic, it offers an excellent indication. You should take the email with a grain of salt if you notice a failure or soft fail outcome.
Watch Out for Strange Emails Uses of BCC Fields
Your email address could be listed in the Bcc field of certain emails rather than the recipient lines. Although there’s nothing wrong with maintaining the recipient in the Bcc box, this is uncommon for companies to do when communicating with consumers.
For instance, to validate your account details or to ask consumers to download transaction receipts, no legitimate business would send a blind carbon copy email. Why? Since they would contact you immediately.
Therefore, it’s a good indication that the email is a scam if your email address appears in the Bcc area rather than before “To:” or “Send To:”
Verify to Discover if Embedded Links Redirect to Unknown Websites
Unexpected redirect URLs are another sign of a fraudulent email. The email’s embedded links must lead to the same web page as the one specified in the link. However, fraudsters use language that appears to link to a trustworthy website, but the embedded hyperlinks direct you to a phishing or harmful website.
For instance, you can get an email that appears to be from GoCardless. It notifies you of an unauthorized login attempt and requests a new password to secure your account. You may update your password by visiting www.GoCardless.com/account/passwordChange.
The link appears legitimate, so you decide it is safe to click. However, if you click on this link, you’ll be sent to a fraudulent website that imitates GoCardless’s layout, colors, fonts, and logo to make it look authentic. The bogus website will attempt to fool you into providing your login information or other sensitive information here.
Additionally, the “Unsubscribe” option occasionally conceals harmful redirection.
But how can you determine a link’s validity without clicking on it? In suspicious emails, there are two approaches to looking for bogus links:
1. To see the actual URL for a link, move the cursor over it.
Lingering over a link will reveal the destination to which it redirects. It’s probably a malicious link if the pop-up URL differs from the content that it links to. Delete that click!
2. Click the “Inspect” option from the drop-down menu by right-clicking the question link (or button).
You’ll notice a new window appear with several lines of code on the right side or bottom.
After the text “a href=,” you will notice a URL. It’s the location to which the text or media is linked. In other words, it indicates that following the link will direct you to that URL.
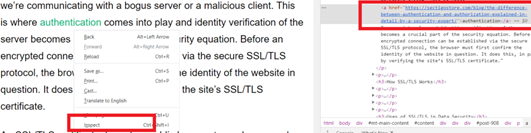
Using this strategy, you can always check suspicious hyperlinks, media, and buttons.
“Someone has access to your Account!” or Other Urgent or Intimidating Phrases.
Hackers want you to respond fast and unknowingly to a scam. And using your emotions is the simplest method to achieve it.
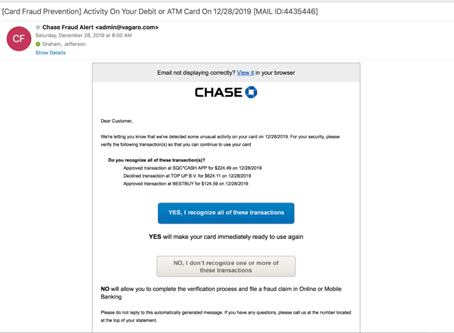
The “scare” method is a common phishing fraud technique. Malicious users deceive you into clicking on a link or downloading a suspicious attachment by instilling a sense of urgency or anxiety.
The allegation that your genuine accounts have already been compromised is one of the most typical phishing messages. With phrases like “Unauthorised login attempt on your account” or “We’ve detected some unusual activity,” they generate emails that appear to be from accounts you trust.
The emails will contain a link that will take you to a place where you must input your login information to ensure your account is secure.
These fraudulent emails can be hard to identify, mainly if they use accounts, you genuinely use.
Moreover, they might reach you about the following topics:
- Unbelievable savings or an incredible deal on the item
- Costly lottery jackpots.
- offering a job
- access to your account without authorization
- Identity theft involves your credentials.
- Accessible credit reports
- An erroneous purchase was made using your account (see the snapshot of Amazon from the preceding paragraph)
- A fundraising effort for the underprivileged, those with uncommon diseases, and those who have suffered natural disasters.
Look at the “From” email address before clicking a link. Is it a genuine organization’s message? Otherwise, it’s a deception.
Always get in touch with any company that reaches you without your consent. Look for a phone number or contact form for customer service on their official website. You can request that they confirm the mail is genuine and not a scam.
Grammatical and Spelling Mistakes
Grammar and spelling errors are common among people. However, there is a trapping technique of hackers for sending strangely phrased or structured scam emails.
It’s a massive red signal that you’re dealing with a fraudster if an email doesn’t read correctly, especially if it pretends to be from a major organization.
As we swiftly read through our inboxes, these mistakes occasionally must be noticed.
You shouldn’t assume that an email with errors in spelling and language is a scam. However, it is a cautionary tale that any additional action should be taken cautiously.
How to Defend Yourself Against Email Hackers and Scammers?
Email scams are not going away. The future will only bring you more of them.
While spam filters are improving at keeping your inbox secure, 96% of phishing attempts still take place over email, resulting in losses of over $323 million.
You can protect your email accounts, identity, and money against fraudsters and cybersecurity dangers in five different ways:
Don’t Open any Attachments or Open Any Links
Do not open files or click on links in emails you have reason to believe are not genuine. Instead, phone the source or investigate to confirm the contact’s identity. Scammers occasionally provide their contact information in emails. Use them not. Do your research instead.
Software Updates must always be Addressed
Usually, scammers use obsolete software and operating systems to implant malware and other infections. To prevent exposing your data to cyber threats like zero-day vulnerability attacks, update your software often.
Never Respond to Spam Emails
Delete an email if it comes from someone you don’t know or if anything about it seems rushed. You are more likely to get similar scam emails if you reply to a scam email since doing so lets the fraudster know that your address is active.
Set up Phishing and Antivirus Protection Software
Manually scanning every email, you get for fraud takes time and effort and doesn’t provide 100% security. Quarantining any dangerous information and installing antivirus and phishing prevention software can help screen and protect all your emails.
Be Careful while Disclosing Personal Information
Hackers utilize social engineering techniques to deceive you into disclosing personal information, such as sending you an email out of the blue from someone pretending to be a long-time friend. When you get an email of this type, don’t reply, or reveal any personal information, not even your name.
You use your email for everything, including communicating with friends and paying payments regularly. And because of that, hackers and fraudsters target it constantly.
To protect your accounts, follow these recommendations.
Final words!
We observed that a single email could expose a typically secure workplace to potential hazards. It may result in financial consequences and harm the business’s reputation and trust among investors and consumers.
Cybercriminals are developing creative techniques to persuade users to divulge crucial personal data. As a result, we must verify all the information about an email sender before making any substantial decisions, such as transferring money or disclosing personal information. Therefore, determining whether an email is legitimate or bogus is significant.
People and organizations must be alert to bogus emails as the frequency of scams increases. You can acquire an inherent ability to distinguish between genuine and fraudulent emails by following the rules mentioned in this article.
Always be alert for suspicious emails, believe in your instincts, and check them out before responding. Doing this will significantly lower your chance of being a victim of fraud and secure your privacy.